Plasticizer
[1] Plasticizers are also often added to concrete formulations to make them more workable and fluid for pouring, thus allowing the water contents to be reduced.
Similarly, they are often added to clays, stucco, solid rocket fuel, and other pastes prior to molding and forming.
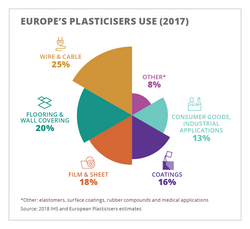
In North America the 2017 volume was ~1.01 million metric tonnes and in Europe the figure was 1.35 million metric tonnes, split between various end-use applications with a chemical type trend moving to higher molecular weight (HMW) orthophthalates and alternative types following regulatory issues concerning lower molecular weight (LMW) orthophthalates.
Almost 90% of polymer plasticizers, most commonly phthalate esters, are used in PVC, giving this material improved flexibility and durability.
The wide variety of ester chemistries that are in production include sebacates, adipates, terephthalates, dibenzoates, glutarates, phthalates, azelates, and other specialty blends.
Low to high polarity esters provide utility in a wide range of elastomers including nitrile, polychloroprene, EPDM, chlorinated polyethylene, and epichlorohydrin.
These compounds are selected on the basis of many critieria including low toxicity, compatibility with the host material, nonvolatility, and expense.
Phthalate esters of straight-chain and branched-chain alkyl alcohols meet these specifications and are common plasticizers.
Substantial concerns have been expressed over the safety of some polymer plasticizers, especially because some low molecular weight ortho-phthalates have been classified as potential endocrine disruptors with some developmental toxicity reported.
Traditional lignosulfonate-based plasticisers, naphthalene and melamine sulfonate-based superplasticisers disperse the flocculated cement particles through a mechanism of electrostatic repulsion (see colloid).
The sugars, chelating agents in lignosulfonates such as aldonic acids and extractive compounds are mainly responsible for set retardation.
These low range water reducing dispersants are commonly manufactured from lignosulfonates, a by-product from the paper industry.
High range superplasticizers (dispersants) have generally been manufactured from sulfonated naphthalene condensate, although polycarboxylic ethers represent more modern alternatives.
[18] Traditional lignosulfonate and naphthalene sulfonate-based plasticisers disperse the flocculated gypsum particles through a mechanism of electrostatic repulsion (see Colloid).
Energetic plasticizers reduce the required mass of propellant, enabling a rocket vehicle to carry more payload or reach higher velocities than would otherwise be the case.
Here are some energetic plasticizers used in rocket propellants and smokeless powders: Due to the secondary alcohol groups, NG and BTTN have relatively low thermal stability.