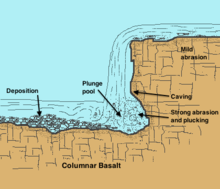
Plunge pool
[2] Plunge pools are formed by the natural force of falling water, such as at a waterfall or cascade; they also result from man-made structures such as some spillway designs.
[4] The impacting and swirling water, sometimes carrying rocks within it, abrades the riverbed into a basin, which often features rough and irregular sides.
[5] They can also be found underwater in areas that were formerly above sea level, for example, Perth Canyon off the coast of Western Australia.
Plunge pools are fluvial features of erosion which occur in the youthful stage of river development, characterized by steeper gradients and faster water flows.
Because this rock is often less resistant than overlying strata, the water from the higher elevation continues eroding downward until an equilibrium is achieved.