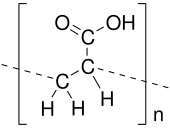
Polyacrylic acid
In addition to the homopolymers, a variety of copolymers and crosslinked polymers, and partially deprotonated derivatives thereof, are known and of commercial value.
Partially or wholly deprotonated PAAs are polyelectrolytes, with the ability to absorb and retain water and swell to many times their original volume.
[15][16] Polyacrylic acid is a weak anionic polyelectrolyte, whose degree of ionisation is dependent on solution pH.
[17] In aqueous solutions PAA can also form polycomplexes with oppositely charged polymers such as chitosan, surfactants, and drug molecules (for example, streptomycin).
Acrylic acid is also the main component of Superabsorbent Polymers (SAPs), which are cross-linked polyacrylates that can absorb and retain more than 100 times of their own weight in liquid.
They stabilize suspended solid in liquids,[22] prevent emulsions from separating, and control the consistency in flow of cosmetics.
[23] A few reports were made on PAA use as deflocculant (so called alkaline polyacrylates) for oil drilling industry.