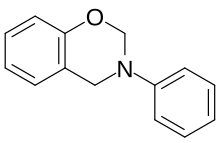
Polybenzoxazine
Numerous research focus on the different curing temperature, and polymer properties, such as cross-linking, from benzoxazines derived from substituted phenols.
[citation needed] The result of heating up benzoxazine monomers is a high molecular weight thermoset polymer matrix.
Because of their superior resistance to chemicals, low flammability, and excellent heat stability, they are used for components that are exposed to high temperatures and corrosive media.
Examples include chemical and heat resistant coatings, adhesives, prepregs, and encapsulants as well as halogen-free laminates for printed circuit boards.
Polybenzoxazines are also used in the automotive and aerospace industries for applications where superior thermal and mechanical properties relative to conventional resins are required.