Pulpotomy
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure performed in children on a primary tooth with extensive caries but without evidence of root pathology.
[2] There are various types of medicament placed above the vital pulp such as Buckley's Solution of formocresol, ferric sulfate, calcium hydroxide or mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA).
Examples include teeth with carious exposures and trauma in which treatment of the exposed pulp is delayed and it becomes necessary to extend farther into the canal to reach healthy tissue.
[6] After the pulpotomy treatment, the radicular pulp should remain asymptomatic without any adverse clinical signs or symptoms such as sensitivity, pain, or swelling.
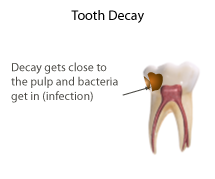
When the soft tissue in the pulp chamber is infected (has bacteria in it) or affected (is inflamed), it can be removed by a dentist or dental therapist under local anaesthetic.
There are many medicaments that can be used to fill the pulp chamber, including zinc oxide eugenol as well as mineral trioxide aggregate.
However, recent research shows that non-vital pulpotomies are rarely indicated due to their low success rates and it is therefore sometimes better to extract the tooth.
Due to the process of a pulpotomy causing the tooth to become slightly brittle, a stainless steel crown is normally indicated as the preferred choice of definitive restoration.
In recent years, glutaraldehyde has been proposed as an alternative to formocresol based on: its superior fixative properties and low toxicity.
In this case, the tooth should be filled with noxious restorative materials within, thereby diminishing the chances of internal resorption, as well as formation of reparative dentin.
[8] Partial pulpotomy is also indicated in young permanent teeth with pulp exposure due to caries, provided that the bleeding can be controlled within several minutes.
[12] In primary teeth medicaments such as formocresol, mineral trioxide aggregate, zinc oxide eugenol and calcium hydroxide can be used in pulpotomy.
[13] Ferric sulfate, sodium hypochlorite[14][15] or a local anaesthetic solution containing a vasoconstrictor agent can be used to arrest any bleeding from the pulp prior to the placement of medicament.
Calcium enriched mixtures have been used in permanent molar teeth with irreversible pulpitis showing positive outcomes.
The physiological clot formation is thought to be able to minimize inflammation and internal resorption compared to calcium hydroxide.
This action fastens the vital pulp, maintaining them inert and conserves the primary tooth until it falls off physiologically.
[19][20] After pulpal bleeding is arrested, a suitable base such as zinc oxide eugenol is placed to seal the tooth from microleakage.
[12][21] Therefore, in spite being a popular vital pulp therapy material, its use as a pulpotomy agent remains controversial.
[1][12] Electro-surgical pulpotomy is a method of cutting and coagulating soft tissues by means of high frequency radio waves.
[19][23] The carbon-dioxide laser emits an infrared beam that has an affinity for water, and is capable of producing well-localized cautery to soft tissue.
[24] Conserving the vitality of pulp tissues appears to be a less painful alternative to root canal treatment (RCT) for younger patients.
The high success rate reported for pulpotomy suggests that this procedure offers hope as an alternative to root canal treatment in teeth with a diagnosis of irreversible pulpitis.