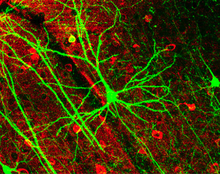
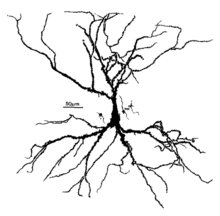
Pyramidal cell
[1] Pyramidal neurons are also one of two cell types where the characteristic sign, Negri bodies, are found in post-mortem rabies infection.
Ramón y Cajal was also the first person to propose the physiological role of increasing the receptive surface area of the neuron.
Endocannabinoids (eCBs) are one class of molecules that have been shown to direct pyramidal cell development and axonal pathfinding.
[11][12] Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in pyramidal cell dendrites are activated by subthreshold EPSPs and by back-propagating action potentials.
[13] The ability of pyramidal neurons to integrate information depends on the number and distribution of the synaptic inputs they receive.
[1] Pyramidal neurons have been classified into different subclasses based upon their firing responses to 400-1000 millisecond current pulses.
For example, pyramidal cells of layer 2-3 in human are classified as FREM3 type[16] and often have a high amount of Ih-current[19] generated by HCN-channel.
Normal motor control depends on the development of connections between the axons in the corticospinal tract and the spinal cord.
With proper connections, pyramidal cells take part in the circuitry responsible for vision guided motor function.
[21] These cells might also play a critical role in complex object recognition within the visual processing areas of the cortex.
[3] Relative to other species, the larger cell size and complexity of pyramidal neurons, along with certain patterns of cellular organization and function, correlates with the evolution of human cognition.
They form synapses that aid in the integration of synaptic voltages throughout their complex dendritic trees through interactions with mossy fibers from granule cells.
Since it affects the postsynaptic voltages produced by mossy fiber activation, the placement of thorny excrescences on basal and apical dendrites is important for memory formation.
Fundamentally, mossy fiber input is received by pyramidal cells in the hippocampus which integrate synaptic voltages within their dendritic architecture.
The location of prickly protrusions and the clustering of synapses influence sensitivity and contribute to the processing of information pertaining to memory and learning.