Pythagorean trigonometric identity
The Pythagorean trigonometric identity, also called simply the Pythagorean identity, is an identity expressing the Pythagorean theorem in terms of trigonometric functions.
Along with the sum-of-angles formulae, it is one of the basic relations between the sine and cosine functions.
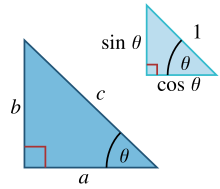
Any similar triangles have the property that if we select the same angle in all of them, the ratio of the two sides defining the angle is the same regardless of which similar triangle is selected, regardless of its actual size: the ratios depend upon the three angles, not the lengths of the sides.
Thus for either of the similar right triangles in the figure, the ratio of its horizontal side to its hypotenuse is the same, namely cos θ.
The elementary definitions of the sine and cosine functions in terms of the sides of a right triangle are:
This definition is valid for all angles, due to the definition of defining x = cos θ and y sin θ for the unit circle and thus x = c cos θ and y = c sin θ for a circle of radius c and reflecting our triangle in the y-axis and setting a = x and b = y. Alternatively, the identities found at Trigonometric symmetry, shifts, and periodicity may be employed.
By the periodicity identities we can say if the formula is true for −π < θ ≤ π then it is true for all real θ.
Next we prove the identity in the range π/2 < θ ≤ π.
We can then make use of squared versions of some basic shift identities (squaring conveniently removes the minus signs):
Finally, it remains is to prove the formula for −π < θ < 0; this can be done by squaring the symmetry identities to get
are also called Pythagorean trigonometric identities.
In this way, this trigonometric identity involving the tangent and the secant follows from the Pythagorean theorem.
The angle opposite the leg of length 1 (this angle can be labeled φ = π/2 − θ) has cotangent equal to the length of the other leg, and cosecant equal to the length of the hypotenuse.
In that way, this trigonometric identity involving the cotangent and the cosecant also follows from the Pythagorean theorem.
The unit circle centered at the origin in the Euclidean plane is defined by the equation:[2] Given an angle θ, there is a unique point P on the unit circle at an anticlockwise angle of θ from the x-axis, and the x- and y-coordinates of P are:[3]
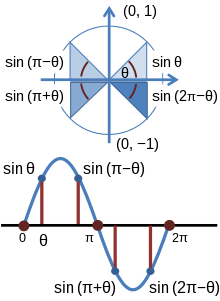
As θ increases from zero to the full circle θ = 2π, the sine and cosine change signs in the various quadrants to keep x and y with the correct signs.
The figure shows how the sign of the sine function varies as the angle changes quadrant.
Because the x- and y-axes are perpendicular, this Pythagorean identity is equivalent to the Pythagorean theorem for triangles with hypotenuse of length 1 (which is in turn equivalent to the full Pythagorean theorem by applying a similar-triangles argument).
See Unit circle for a short explanation.
The trigonometric functions may also be defined using power series, namely for x (an angle measured in radians):[4][5]
The remaining terms of their sum are (with common factors removed)
When the trigonometric functions are defined in this way, the identity in combination with the Pythagorean theorem shows that these power series parameterize the unit circle, which we used in the previous section.
This definition constructs the sine and cosine functions in a rigorous fashion and proves that they are differentiable, so that in fact it subsumes the previous two.
Sine and cosine can be defined as the two solutions to the differential equation:[6]
It follows from the theory of ordinary differential equations that the first solution, sine, has the second, cosine, as its derivative, and it follows from this that the derivative of cosine is the negative of the sine.
The identity is equivalent to the assertion that the function
A calculation confirms that z(0) = 1, and z is a constant so z = 1 for all x, so the Pythagorean identity is established.
A similar proof can be completed using power series as above to establish that the sine has as its derivative the cosine, and the cosine has as its derivative the negative sine.
In fact, the definitions by ordinary differential equation and by power series lead to similar derivations of most identities.
This proof of the identity has no direct connection with Euclid's demonstration of the Pythagorean theorem.