Quantization (signal processing)
to the nearest integer value forms a very basic type of quantizer – a uniform one.
Adding one bit to the quantizer halves the value of Δ, which reduces the noise power by the factor 1/4.
[6] The input and output sets involved in quantization can be defined in a rather general way.
Quantization replaces each real number with an approximation from a finite set of discrete values.
Rate–distortion optimized quantization is encountered in source coding for lossy data compression algorithms, where the purpose is to manage distortion within the limits of the bit rate supported by a communication channel or storage medium.
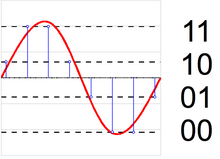
Most uniform quantizers for signed input data can be classified as being of one of two types: mid-riser and mid-tread.
The terminology is based on what happens in the region around the value 0, and uses the analogy of viewing the input-output function of the quantizer as a stairway.
The input-output formula for a mid-riser uniform quantizer is given by: where the classification rule is given by and the reconstruction rule is Note that mid-riser uniform quantizers do not have a zero output value – their minimum output magnitude is half the step size.
The dead zone can sometimes serve the same purpose as a noise gate or squelch function.
A very commonly used special case (e.g., the scheme typically used in financial accounting and elementary mathematics) is to set
A common assumption for the analysis of quantization error is that it affects a signal processing system in a similar manner to that of additive white noise – having negligible correlation with the signal and an approximately flat power spectral density.
[6][14] In the typical case, the original signal is much larger than one least significant bit (LSB).
When this is the case, the quantization error is not significantly correlated with the signal and has an approximately uniform distribution.
When rounding is used to quantize, the quantization error has a mean of zero and the root mean square (RMS) value is the standard deviation of this distribution, given by
Although rounding yields less RMS error than truncation, the difference is only due to the static (DC) term of
At lower amplitudes the quantization error becomes dependent on the input signal, resulting in distortion.
It is a rounding error between the analog input voltage to the ADC and the output digitized value.
When the input signal has a high amplitude and a wide frequency spectrum this is the case.
The 1.761 difference in signal-to-noise only occurs due to the signal being a full-scale sine wave instead of a triangle or sawtooth.
[17] In these cases the quantization noise distribution is strongly affected by the exact amplitude of the signal.
A technique for controlling the amplitude of the signal (or, equivalently, the quantization step size
which optimally satisfy a selected set of design constraints such as the bit rate
Solutions that do not require multi-dimensional iterative optimization techniques have been published for only three PDFs: the uniform,[18] exponential,[12] and Laplacian[12] distributions.
For the mean-square error distortion criterion, it can be easily shown that the optimal set of reconstruction values
to the conditional expected value (also referred to as the centroid) within the interval, as given by: The use of sufficiently well-designed entropy coding techniques can result in the use of a bit rate that is close to the true information content of the indices
Lloyd's Method I algorithm, originally described in 1957, can be generalized in a straightforward way for application to vector data.
Moreover, the technique can be further generalized in a straightforward way to also include an entropy constraint for vector data.
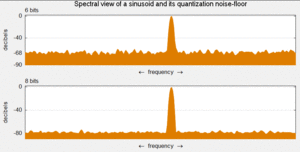
The property of 6 dB improvement in SQNR for each extra bit used in quantization is a well-known figure of merit.
However, it is common to assume that for many sources, the slope of a quantizer SQNR function can be approximated as 6 dB/bit when operating at a sufficiently high bit rate.
At asymptotically high bit rates, the 6 dB/bit approximation is supported for many source PDFs by rigorous theoretical analysis.