Radiative process
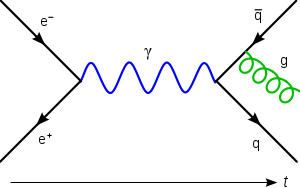
In particle physics, a radiative process refers to one elementary particle emitting another and continuing to exist.
[1] This typically happens when a fermion emits a boson such as a gluon or photon.
This particle physics–related article is a stub.
You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.