nth root
The positive integer n is called the index or degree, and the number x of which the root is taken is the radicand.
, is the inverse of raising a number to the nth power,[1] and can be written as a fractional exponent:
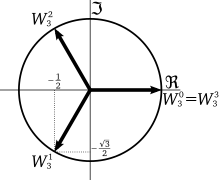
In general, any non-zero complex number has n distinct complex-valued nth roots, equally distributed around a complex circle of constant absolute value.
Extracting the nth roots of a complex number x can thus be taken to be a multivalued function.
As a function, the principal root is continuous in the whole complex plane, except along the negative real axis.
The nth roots of 1 are called roots of unity and play a fundamental role in various areas of mathematics, such as number theory, theory of equations, and Fourier transform.
An archaic term for the operation of taking nth roots is radication.
The term "surd" traces back to Al-Khwarizmi (c. 825), who referred to rational and irrational numbers as audible and inaudible, respectively.
This later led to the Arabic word أصم (asamm, meaning "deaf" or "dumb") for irrational number being translated into Latin as surdus (meaning "deaf" or "mute").
Gerard of Cremona (c. 1150), Fibonacci (1202), and then Robert Recorde (1551) all used the term to refer to unresolved irrational roots, that is, expressions of the form
are integer numerals and the whole expression denotes an irrational number.
is rational, are called pure quadratic surds; irrational numbers of the form
Expressing the degree of an nth root in its exponent form, as in
Subtleties can occur when taking the nth roots of negative or complex numbers.
strictly holds for non-negative real radicands only, its application leads to the inequality in the first step above.
The nth root of a number A can be computed with Newton's method, which starts with an initial guess x0 and then iterates using the recurrence relation
For computational efficiency, the recurrence relation is commonly rewritten
Newton's method can be modified to produce various generalized continued fractions for the nth root.
Using this more general expression, any positive principal root can be computed, digit-by-digit, as follows.
Algorithm terminates: Answer is 12.34 Find the cube root of 4192 truncated to the nearest thousandth.
The principal nth root of a positive number can be computed using logarithms.
This can be found by first multiplying both sides of the defining equation by −1 to obtain
In 1837 Pierre Wantzel proved that an nth root of a given length cannot be constructed if n is not a power of 2.
which introduces a branch cut in the complex plane along the positive real axis with the condition 0 ≤ θ < 2π, or along the negative real axis with −π < θ ≤ π.
The last branch cut is presupposed in mathematical software like Matlab or Scilab.
These roots are evenly spaced around the unit circle in the complex plane, at angles which are multiples of
In polar form, a single nth root may be found by the formula
Thus finding nth roots in the complex plane can be segmented into two steps.
Second, the angle between the positive horizontal axis and a ray from the origin to one of the nth roots is
As with square roots, the formula above does not define a continuous function over the entire complex plane, but instead has a branch cut at points where θ / n is discontinuous.

none of which are real

one of which is a negative real






![{\displaystyle y={\sqrt[{3}]{x}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/be50c0a49b200fb46800951d0268b0a9d4e3fdda)
