Elementary arithmetic
Elementary arithmetic is a branch of mathematics involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Due to its low level of abstraction, broad range of application, and position as the foundation of all mathematics, elementary arithmetic is generally the first branch of mathematics taught in schools.
[1][2] In numeral systems, digits are characters used to represent the value of numbers.
[4] Regardless of the numeral system used, the results of arithmetic operations are unaffected.
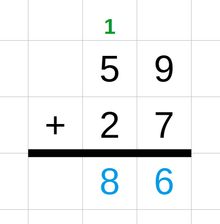
Addition is a mathematical operation that combines two or more numbers (called addends or summands) to produce a combined number (called the sum).
[9] In elementary arithmetic, students typically learn to add whole numbers and may also learn about topics such as negative numbers and fractions.
The minus sign is also used to notate negative numbers.
[10] Subtraction is not commutative, which means that the order of the numbers can change the final value;
In elementary arithmetic, the minuend is always larger than the subtrahend to produce a positive result.
[11] Reform mathematics is distinguished generally by the lack of preference for any specific technique, replaced by guiding students to invent their own methods of computation.
American schools teach a method of subtraction using borrowing.
Subtracting 9 from 6 involves borrowing a 10 from the tens place, making the problem into
These markings are called "crutches", which were invented by William A. Brownell, who used them in a study, in November 1937.
In contrast to the previous method, no borrowing is used, although there are crutches that vary according to certain countries.
[14][15] The method of addition involves augmenting the subtrahend.
A small 1 is marked below the subtrahend digit as a reminder.
Subtracting the numbers 792 and 308, starting with the ones column, 2 is smaller than 8.
Multiplication is a mathematical operation of repeated addition.
The statement "five times three equals fifteen" can be written as "
The product of 2 and 3 is 6, and the carry digit adds 2 to 6, so 8 is written under the tens column.
The result: Multiplying 789 and 345, starting with the ones column, the product of 789 and 5 is 3945.
Adding all the products, The result: Division is an arithmetic operation, and the inverse of multiplication, given that
In English usage, the colon is restricted to the concept of ratios ("a is to b").
Division by zero is considered impossible at an elementary arithmetic level.
Two numbers can be divided on paper using long division.
A less systematic method involves the concept of chunking, involving subtracting more multiples from the partial remainder at each stage.
Dividing 272 and 8, starting with the hundreds digit, 2 is not divisible by 8.
The largest number that the divisor of 8 can be multiplied by without exceeding 27 is 3, so it is written under the tens column.
Elementary arithmetic is typically taught at the primary or secondary school levels and is governed by local educational standards.
There has been debate about the content and methods used to teach elementary arithmetic in the United States and Canada.