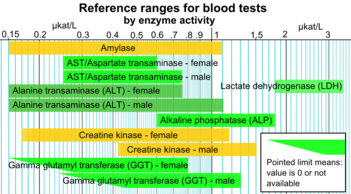
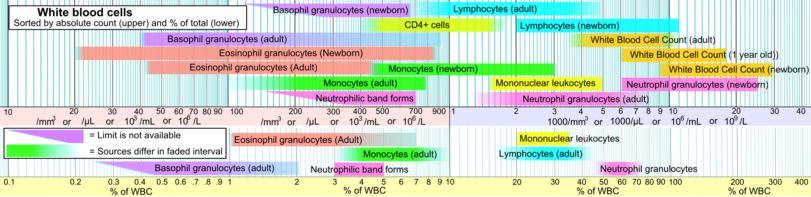
Reference ranges for blood tests
Reference ranges for blood tests are studied within the field of clinical chemistry (also known as "clinical biochemistry", "chemical pathology" or "pure blood chemistry"), the area of pathology that is generally concerned with analysis of bodily fluids.
[1] A reference range is usually defined as the set of values 95 percent of the normal population falls within (that is, 95% prediction interval).
More specifically, optimal levels are generally close to a central tendency of the values found in the population.
[7][8][9] References range may vary with age, sex, race, pregnancy,[10] diet, use of prescribed or herbal drugs and stress.
[12] Smaller, narrower boxes indicate a more tight homeostatic regulation when measured as standard "usual" reference range.
Hormones predominate at the left part of the scale, shown with a red at ng/L or pmol/L, being in very low concentration.
For example, on a certain monitor, the horizontal distance between the upper limits for parathyroid hormone in pmol/L and pg/mL may be 7 cm, with the mass concentration to the right.
Included here are also related binding proteins, like ferritin and transferrin for iron, and ceruloplasmin for copper.
[44] (high sensitive) The diagrams below take inter-cycle and inter-woman variability into account in displaying reference ranges for estradiol, progesterone, FSH and LH.