Volume overload
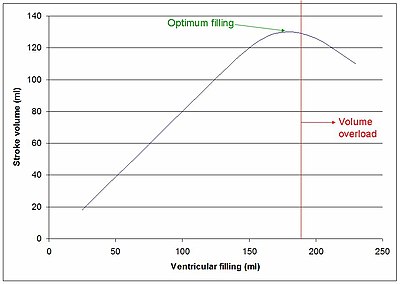
Ventricular volume overload is approximately equivalent to an excessively high preload.
[1] In accordance with the Frank–Starling law of the heart, the myocardium contracts more powerfully as the end-diastolic volume increases.
[citation needed] Various pathologies, listed below, can lead to volume overload.
Different mechanisms are involved depending on the cause, however the common theme is that of a high cardiac output with a low or normal afterload.
[citation needed] Left ventricular volume overload may produce inverted u waves on the electrocardiogram.