5 ft and 1520 mm gauge railways
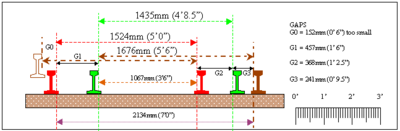
In 1827, Horatio Allen, the chief engineer of the South Carolina Canal and Rail Road Company, prescribed the usage of 5 ft (1,524 mm) gauge.
The presence of several distinct gauges was a major disadvantage to the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War.
[5] In 1837, the first railway built in Russia was a 6 ft (1,829 mm) gauge, 17 km long experimental line connecting Saint Petersburg with Tsarskoye Selo and Pavlovsk.
The choice of gauge was influenced by Brunel's Great Western Railway which used 7 ft (2,134 mm).
It was a 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge, with the express intention of allowing through-freight trains into Austria-Hungary.
There, the Tsar established a committee to recommend technical standards for the building of Russia's first major railway.
The team included devotees of Franz Anton von Gerstner, who pushed to continue the Tsarskoye Selo gauge, and engineer Pavel Melnikov and his consultant George Washington Whistler, a prominent American railway engineer.
By the time difficulties arose in connecting the Prussian railroads to the Russian ones in Warsaw in the 1850s, it was too late to change.
[8] The Russian military recognized as early as 1841 that operations to disrupt railway track did not depend on the gauge, and should instead focus on destroying bridges and tunnels.
[6][7] However, in both World Wars the break of gauge did pose some amount of obstacle to the invading Germans.
Unlike in South Manchuria, the Soviet Union's reconquest of southern Sakhalin from Japan did not result in regauging of the railway system.
The original gauge was chosen under the influence of the pre-conversion southern United States railway companies.
The electric manoeuvering locomotives along the locks (mules) still use the 5 ft gauge that was laid during canal construction.
As the running gear (wheelsets) of the rolling stock remained unaltered, the result was an increased speed and stability.
[14] In Finland, the Finnish State Railways kept the original definition of 1,524 mm (5 ft), even though they also have tightened the tolerances in a similar way, but to a higher level.
[20] There is an approximately 150 km long section in Hungary in the Záhony logistics area close to the Ukrainian border.
[21] Following renovations in 2014, a 32 km section of dual Standard/Russian gauge was installed between Tumangang and Rajin stations in North Korea.
[22] The most western 1,520 mm gauge railway is the Polish LHS (Linia Hutnicza Szerokotorowa) from the Ukrainian border to the eastern end of the Upper Silesian Industrial Region.