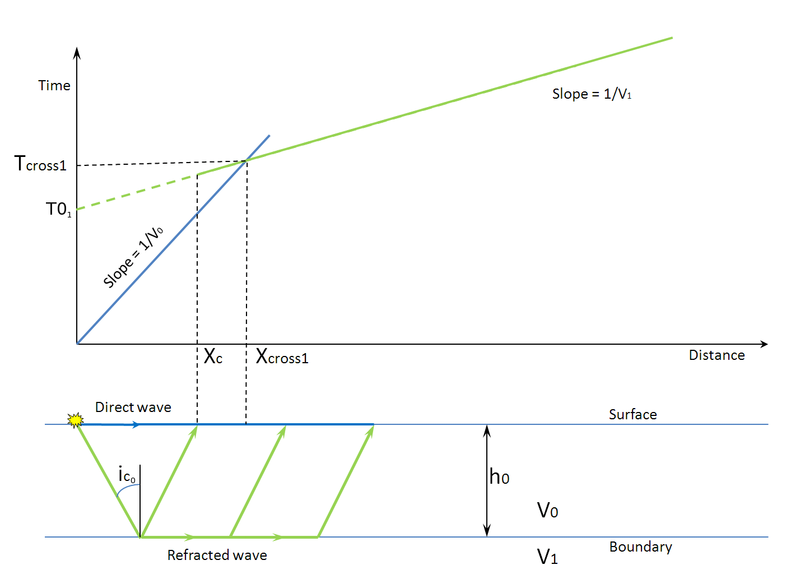
Seismic refraction
The waves are refracted when they cross the boundary between different types (or conditions) of soil or rock.
The methods enable the general soil types and the approximate depth to strata boundaries, or to bedrock, to be determined.
P-wave refraction evaluates the compression wave generated by the seismic source located at a known distance from the array.
S-wave refraction evaluates the shear wave generated by the seismic source located at a known distance from the array.
Seismic refraction has been successfully applied to tailings characterisation through P- and S-wave travel time tomographic inversions.