Servo control
The PWM signal might come from a radio control receiver to the servo or from common microcontrollers such as the Arduino.
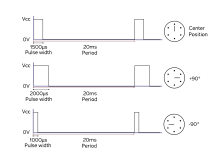
In modern RC servos the angle of mechanical rotation is determined by the width of an electrical pulse that is applied to the control wire.
Modern RC servo position is not defined by the PWM duty cycle (i.e., ON vs. OFF time) but only by the width of the pulse.
With many RC servos, as long as the refresh rate (how many times per second the pulse is sent, a.k.a.
[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9] The period of 20 ms (50 Hz) comes from the days where the signal was encoded in PPM (pulse-position modulation) format to be sent over the air.
However, it is possible to command an RC servo to move over its entire range with a function generator set to a constant 10% duty cycle by changing only the frequency (frame rate).