Sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis may also develop because of the presence of existing chronic infection of the glands, dehydration (e.g. use of phenothiazines), Sjögren's syndrome and/or increased local levels of calcium, but in many instances the cause is idiopathic (unknown).
Sialolithiasis is common, accounting for about 50% of all disease occurring in the major salivary glands and causing symptoms in about 0.45% of the general population.
A calculus (plural calculi) is a hard, stone-like concretion that forms within an organ or duct inside the body.
However, calculi are not the only reasons that a salivary gland may become blocked and give rise to the meal time syndrome.
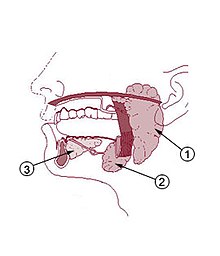
[4] Submandibular stones are further classified as anterior or posterior in relation to an imaginary transverse line drawn between the mandibular first molar teeth.
Signs and symptoms are variable and depend largely upon whether the obstruction of the duct is complete or partial, and how much resultant pressure is created within the gland.
Initially, factors such as abnormalities in calcium metabolism,[3] dehydration,[2] reduced salivary flow rate,[2] altered acidity (pH) of saliva caused by oropharyngeal infections,[2] and altered solubility of crystalloids,[2] leading to precipitation of mineral salts, are involved.
[1] The next stage involves the formation of a nidus which is successively layered with organic and inorganic material, eventually forming a calcified mass.
Fragments of bacteria from salivary calculi were reported to be Streptococci species which are part of the normal oral microbiota and are present in dental plaque.
[3] The flow of saliva from the submandibular gland is often against gravity due to variations in the location of the duct orifice.
[3] These factors all promote slowing and stasis of saliva in the submandibular duct, making the formation of an obstruction with subsequent calcification more likely.