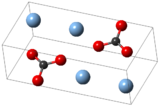
Silver carbonate
This salt is yellow but typical samples are grayish due to the presence of elemental silver.
It is poorly soluble in water, like most transition metal carbonates.
[8] Freshly prepared silver carbonate is colourless, but the solid quickly turns yellow.
[9] Silver carbonate reacts with ammonia to give the diamminesilver(I) ([Ag(NH3)2]+) complex ion.
[12] In the Fétizon oxidation, silver carbonate on Celite[13] serves as an oxidising agent to form: In the Koenigs-Knorr reaction it is used to convert alkyl bromides to the methyl ethers.