Skin flora
[3] A major non-human skin flora is Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a chytrid and non-hyphal zoosporic fungus that causes chytridiomycosis, an infectious disease thought to be responsible for the decline in amphibian populations.
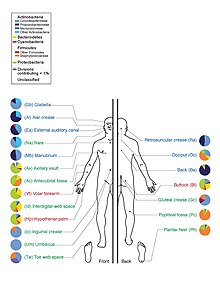
The study showed a large fungal diversity across the body, the richest habitat being the heel, which hosts about 80 species of fungi.
[13] The Belly Button Biodiversity Project began at North Carolina State University in early 2011 with two initial groups of 35 and 25 volunteers.
)[18] According to the Belly Button Biodiversity Project[10] at North Carolina State University, there are two types of microorganisms found in the navel and surrounding areas.
[25] So important is its antimicrobial actions that it has been noted that "removing P. aeruginosa from the skin, through use of oral or topical antibiotics, may inversely allow for aberrant yeast colonization and infection.
Sweat is odorless however several bacteria may consume it and create byproducts which may be considered putrid by humans (as in contrast to flies, for example, that may find them attractive/appealing).
Cathelicidins not only reduce microbe numbers directly but also cause the secretion of cytokine release which induces inflammation, angiogenesis, and reepithelialization.
[31] Another factor affecting the growth of pathological bacteria is that the antimicrobial substances secreted by the skin are enhanced in acidic conditions.
Skin fungi such as Trichophyton rubrum have evolved to create substances that limit the immune response to them.
[39][40] Current treatment includes topical and systemic antibacterial drugs which result in decreased C. acnes colonisation and/or activity.
[42] Lactobacillus plantarum has also been shown to act as an anti-inflammatory and improve antimicrobial properties of the skin when applied topically.
[43] Individuals with atopic dermatitis have shown an increase in populations of Staphylococcus aureus in both lesional and nonlesional skin.
[citation needed] Current treatments include combinations of topical or systemic antibiotics, corticosteroids, and diluted bleach baths.
[44] Potential probiotic treatments include using the commensal skin bacteria, S. epidermidis, to inhibit S. aureus growth.
[45] (See gut microbiota) Psoriasis vulgaris typically affects drier skin sites such as elbows and knees.
Dry areas of the skin tend to have high microbial diversity and fewer populations than sebaceous sites.
[48] Current research on the skin microbiota's role in psoriasis is inconsistent therefore there are no potential probiotic treatments.
Although it is a part of the commensal skin microbiota, patients affected with rosacea show an increase in D. folliculorum compared to healthy individuals, suggesting pathogenicity.
[49] Bacillus oleronius, a Demodex associated microbe, is not typically found in the commensal skin microbiota but initiates inflammatory pathways whose starting mechanism is similar to rosacea patients.
[51] As current research has yet to show a clear mechanism for Demodex influence in rosacea, there are no potential probiotic treatments.
[52] The human skin is host to numerous bacterial and fungal species, some of which are known to be harmful, some known to be beneficial and the vast majority unresearched.
[55] An important use of hand washing is to prevent the transmission of antibiotic resistant skin flora that cause hospital-acquired infections such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
[56] One study of bar soaps in dentist clinics found they all had their own flora and on average from two to five different genera of microorganisms with those used most more likely to have more species varieties.
This can be seen in roughness characterized by scaling and dryness, itchiness, dermatitis provoked by microorganisms and allergens penetrating the corneal layer and redness.
Wearing gloves can cause further problems since it produces a humid environment favoring the growth of microbes and also contains irritants such as latex and talcum powder.
[61] Though not related to greater antibiotic resistance, damaged skin was also more like to be colonized by Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, Enterococci and Candida.