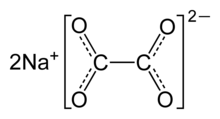
Sodium oxalate
It is only very rarely found and restricted to extremely sodic conditions of ultra-alkaline pegmatites.
Alternatively, it can be produced by decomposing sodium formate by heating it at a temperature exceeding 360 °C.
It is desirable that the temperature of the titration mixture be greater than 60 °C to ensure that all the permanganate added reacts quickly.
It can cause burning pain in the mouth, throat and stomach, bloody vomiting, headache, muscle cramps, cramps and convulsions, drop in blood pressure, heart failure, shock, coma, and possible death.
Sodium oxalate, like citrates, can also be used to remove calcium ions (Ca2+) from blood plasma.