Solar power in the United States
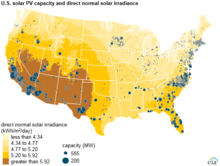
[2] As of the end of 2023, the United States had 179 gigawatts (GW) of installed photovoltaic (utility and small scale) and concentrated solar power capacity combined.
[8] The 280 MW Solana Generating Station is a solar power plant near Gila Bend, Arizona, about 70 miles (110 km) southwest of Phoenix, completed in 2013.
[11][12] A 2012 report from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) described technically available renewable energy resources for each state and estimated that urban utility-scale photovoltaics could supply 2,232 TWh/year, rural utility-scale PV 280,613 TWh/year, rooftop PV 818 TWh/year, and CSP 116,146 TWh/year, for a total of almost 400,000 TWh/year, 100 times the consumption of 3,856 TWh in 2011.
[18] This does not include the significant additional health and mortality burden to society from fossil fuel use that makes it even more expensive than it appears.
[19] The Carter administration provided major subsidies for research into photovoltaic technology and sought to increase commercialization in the industry.
[23]: 143 Government subsidies were higher in Germany and Japan, which prompted the industrial supply chain to begin moving from the US to those countries.
[25] The report noted that the cost per kilowatt-hour of solar photovoltaic systems had been dropping, while electricity generated from fossil fuels was becoming more expensive.
An objector at non-profit “Basin and Range Watch” to the Riverside East Solar Energy Zone in the California desert said in 2023 that ‘solar plants create myriad environmental problems, including habitat destruction and “lethal death traps” for birds, which dive at the panels, mistaking them for water ... one project bulldozed 600 acres of designated critical habitat for the endangered desert tortoise, while populations of Mojave fringe-toed lizards and bighorn sheep have also been afflicted.’ The same article included many other examples of how the same solar project had hurt the desert flora and fauna, according to environmentalists.
[90] Another type of distributed generation implemented by a utility company was the world's first grid-connected pole-attached solar panels of Public Service Enterprise Group in New Jersey.
[91][92] As of November 2017[update], there were nearly 5,500 schools in the United States that had solar installations with the total capacity of approximately 910 MW.
[96] However, as prices have rapidly dropped over the last 10 years, and business models have evolved to avoid upfront costs or high credit scores, rooftop solar is trending towards reaching more and more families of all incomes.
[97] Community solar is available in about one third of the states, including MN, NJ, CA, NY, MA and CO.[98] The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 created a large investment into clean energy with the purpose of developing an increase of green jobs.
[99] Thin-film photovoltaics (CdTe and CIGS) were chosen because they can be less expensive to manufacture than crystalline silicon-based solar cells.
[102] Rapidly decreasing photovoltaic prices put General Electric's planned factory in Colorado on hold,[103] and led to the bankruptcy of Konarka Technologies, which had expected to produce 1,000 MW of solar modules per year by 2011, and Solyndra, which defaulted on a $535 million loan guarantee, prompting Republican members of the Energy and Commerce committee to vote to cease accepting new applications to the loan program.
[105] As cadmium, indium, selenium, nanoparticles, and other harmful elements are used in PV solar technology the disposal is similar to the outcomes of electronic waste.
[106][107] A 2021 study by Harvard Business Review indicates that, unless reused, by 2035 the discarded panels would outweigh new units by a factor of 2.56.
[109] A 2022 study found that modules were lasting longer than previously estimated, and said that might result in less PV waste than had been thought.
[146] In 2022, the Inflation Reduction Act enhanced the investment tax credit available for solar; the base was set a 6% with a 5x multiplier if the project satisfied certain prevailing wage and apprenticeship requirements.
In March 2016, Hatch asked the IRS and Treasury Department to demonstrate that the agencies use safeguards and coordinate with each other when reviewing applications for Section 1603 grants.
[152] Goals: In 2018, as part of a trade war between the U.S. and China, US President Trump imposed tariffs on imported solar cells.
[153] On one hand, these tariffs forced the cancellation or scaling down of many projects and restricted the ability of companies to recruit more workers.
[158] Since the devastating Hurricane Maria in 2017, the adoption of solar energy with battery storage in Puerto Rico has grown rapidly.
[172] According to a June 2024 report by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), the archipelago was installing about 4,000 new solar systems per month.
This trend is expected to continue, supported by federal funding programs, including a $500 million effort by the Energy Department to install systems for vulnerable households.
However, the Financial Oversight and Management Board (FOMB), a federal entity overseeing Puerto Rico's finances, opposed this law.
Twenty-one Members of Congress, including Puerto Rico's representative and prominent politicians like Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez and Bernie Sanders, wrote a letter supporting net metering.
Fifteen environmental and community organizations asked President Joe Biden to appoint new FOMB members who would protect solar energy in Puerto Rico.
According to the 2024 report, despite widespread agreement among policymakers, experts, and institutions that renewable energy sources are crucial for Puerto Rico's power grid "those in charge of day-to-day operation are pursuing aggressive plans for natural gas expansion.
"[172] Under the Biden administration, the DOE's Loan Programs Office lent over $1bn towards the development of utility scale solar facilities on the island.
[185] In 2010, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) ruled that states were able to implement above-market feed-in tariffs for specific technologies.