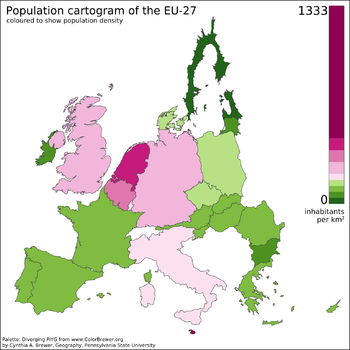
Population density
Examples of the causes of reduced fertility in low population densities are:[2] Population density is the number of people per unit of area, usually transcribed as "per square kilometer" or square mile, and which may include or exclude, for example, areas of water or glaciers.
The world's population is around 8,000,000,000[3] and the Earth's total area (including land and water) is 510,000,000 km2 (200,000,000 sq mi).
[1] The European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC) has developed a suite of (open and free) data and tools named the Global Human Settlement Layer (GHSL) to improve the science for policy support to the European Commission Directorate Generals and Services and as support to the United Nations system.
However, some cities in the Middle East, such as Dubai, have been increasing in population and infrastructure growth at a fast pace.
[8]Cities with high population densities are, by some, considered to be overpopulated, though this will depend on factors like quality of housing and infrastructure and access to resources.