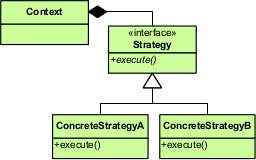
Strategy pattern
Deferring the decision about which algorithm to use until runtime allows the calling code to be more flexible and reusable.
Typically, the strategy pattern stores a reference to code in a data structure and retrieves it.
This can be achieved by mechanisms such as the native function pointer, the first-class function, classes or class instances in object-oriented programming languages, or accessing the language implementation's internal storage of code via reflection.
This is compatible with the open/closed principle (OCP), which proposes that classes should be open for extension but closed for modification.
This approach has significant drawbacks; accelerate and brake behaviors must be declared in each new car model.
Additionally, it is not easy to determine the exact nature of the behavior for each model without investigating the code in each.