Administrative divisions of the Philippines
[1] They are, from the highest to the lowest: Other divisions also exist for specific purposes, such as: Administrative regions are groupings of geographically adjacent LGUs that are established, disestablished, and modified by the president of the Philippines based on the need to more coherently make economic development policies and coordinate the provision of national government services within a larger area beyond the province level.
No plebiscites have been conducted so far to democratically confirm the creation, abolition, or alteration of the boundaries of regular administrative regions, as the Constitution does not mandate it.
The 1987 Constitution allows for the creation of autonomous regions in the Cordillera Central of Luzon and in the Muslim-majority areas of Mindanao.
Per the Local Government Code of 1991, section 25, the President of the Philippines exercises direct supervisory authority over provinces and independent cities (i.e., highly urbanized and independent component cities); thus, LGUs that belong to these categories form the primary level of LGUs in the Philippines.
Pateros, by virtue of not belonging to any province, effectively also constitutes a primary level LGU.
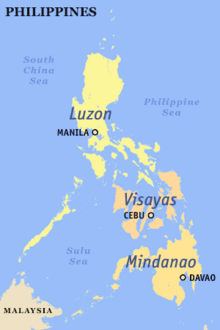
[1] The Philippines is broadly divided into three traditional island groups: Luzon, the Visayas, and Mindanao.
For example, the Palarong Pambansa rotates yearly hosting duties among the island groups, while the League of Municipalities of the Philippines organizes its members and meetings by Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao "clusters.
The 100 zones in Manila serve as an administrative layer immediately below the geographic district level.
Sitios are usually hamlets within rural barangays where human settlement is polycentric, i.e., multiple communities spread across a wide area, separated by farmland, mountains, or water.
Puroks are often neighborhoods or zones in densely populated areas of barangays of more urban character.
However, there are sometimes unofficial arrangements that result in direct representation of purok or sitio interests in the barangay government.
Before voting for inclusion into the ARMM in 2001, Marawi City was also excluded from the first assembly district of Lanao del Sur.
The following table summarizes the number and structure of regions, provinces, cities, municipalities, and barangays in the Philippines as of March 31, 2020.