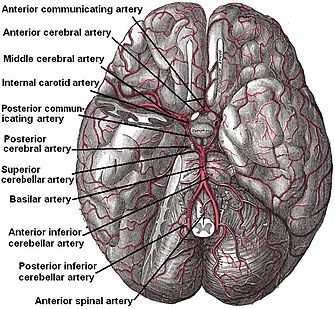
Superior cerebellar artery
[1] When it arrives at the upper surface of the cerebellum, it divides into branches which ramify in the pia mater and anastomose with those of the anterior inferior cerebellar arteries and the posterior inferior cerebellar arteries.
Several branches are given to the pineal body, the anterior medullary velum, and the tela chorioidea of the third ventricle.
[1] The superior cerebellar artery is frequently the cause of trigeminal neuralgia.
[2] At autopsy, 50% of people without trigeminal neuralgia will also be noted to have vascular compression of the nerve.
[4] This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 580 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918) ocular group: central retinal