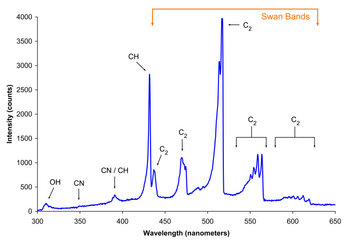
Swan band
Swan bands are a characteristic of the spectra of carbon stars, comets and of burning hydrocarbon fuels.
[1][2] They are named for the Scottish physicist William Swan, who first studied the spectral analysis of radical diatomic carbon (C2) in 1856.
[3] Swan bands consist of several sequences of vibrational bands scattered throughout the visible spectrum.
This astrophysics-related article is a stub.
You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.This spectroscopy-related article is a stub.