TLTx
This toxin selectively inhibits Kv4.2 voltage-gated potassium channels by acting as a gating modifier.
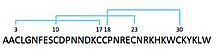
[1] TLTx is part of the family of Kv4-specific tarantula toxins, which are short peptides with a disulfide-bonded core domain.
[4] They form a total of 3 disulfide bonds between the side chains of cysteine, of which the positions in the sequence are identical in all subtypes of the toxin.
The homology with other tarantula toxins suggests that TLTx also forms and inhibitor cystine knot (ICK) motif.
[1] By blocking the transient Kv4.2 potassium channels, TLTx may interfere with action potential repolarisation, leading to prey paralysis.