History of taxation in the United States
They placed a tax on common products imported into the American Colonies, such as lead, paper, paint, glass, and tea.
To increase this revenue, poll taxes were also frequently extended to the process of obtaining hunting, fishing, and driving licenses.
[6] Some poor white male voters were deemed exempt from poll taxes via grandfather clause if they had an ancestor who could vote prior to the Civil War.
Tariffs have played different parts in trade policy and the economic history of the United States.
Tariffs were the largest source of federal revenue from the 1790s to the eve of World War I until it was surpassed by income taxes.
From the 1790s to the present day, the tariff (and closely related issues such as import quotas and trade treaties) generated enormous political stresses.
The schedule of the Morrill Tariff and its two successor bills were retained long after the end of the Civil War.
[13] In 1921, Congress sought to protect local agriculture as opposed to the industry bypassing the Emergency Tariff, which increased rates on wheat, sugar, meat, wool and other agricultural products brought into the United States from foreign nations, which protected domestic producers of those items.
[14] During the outbreak of the Great Depression in 1930, Congress raised tariffs via the Smoot–Hawley Tariff Act on over 20,000 imported goods to record levels, and, in the opinion of most economists, worsened the Great Depression by causing other countries to reciprocate, thereby plunging American imports and exports by more than half.
[15] Federal excise taxes are applied to specific items such as motor fuels, tires, telephone usage, tobacco products, and alcoholic beverages.
During the presidency of George Washington, Alexander Hamilton proposed a tax on distilled spirits to fund his policy of assuming the war debt of the American Revolution for those states which had failed to pay.
After a vigorous debate, the House decided by a vote of 35–21 to approve legislation imposing a seven-cent-per-gallon excise tax on whiskey.
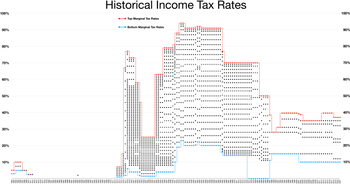
However, the constitutionality of income taxation was widely held in doubt (see Pollock v. Farmers' Loan & Trust Co.) until 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment.
In it, he explains that the wording of the "Necessary and Proper" clause should serve as guidelines for the legislation of laws regarding taxation.
In response to the Supreme Court decision in the Pollock case, Congress proposed the Sixteenth Amendment, which was ratified in 1913,[23] and which states: The Congress shall have the power to lay and collect taxes on incomes, from whatever source derived, without apportionment among the several States, and without regard to any census or enumeration.The Supreme Court in Brushaber v. Union Pacific Railroad, 240 U.S. 1 (1916), indicated that the Sixteenth Amendment did not expand the federal government's existing power to tax income (meaning profit or gain from any source) but rather removed the possibility of classifying an income tax as a direct tax based on the source of the income.
The Amendment removed the need for the income tax on interest, dividends, and rents to be apportioned among the states based on population.
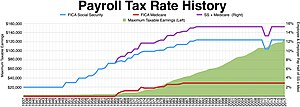
During World War II, Congress introduced payroll withholding and quarterly tax payments.
During World War II, Congress introduced payroll withholding and quarterly tax payments.
[45][46] Ultimately, the combination of base broadening and rate reduction raised revenue equal to about 4% of existing tax revenue[47] For the 1991 and 1992 tax years, the top marginal rate was increased to 31% in a budget deal President George H. W. Bush made with the Congress.
[49] In 2001, President George W. Bush proposed and Congress accepted an eventual lowering of the top marginal rate to 35%.
[50] This measure had a sunset provision and was scheduled to expire for the 2011 tax year when rates would have returned to those adopted during the Clinton years unless Congress changed the law;[51] Congress did so bypassing the Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization and Job Creation Act of 2010, signed by President Barack Obama on December 17, 2010.
Often the receipts intended to be placed in "trust" funds are used for other purposes, with the government posting an IOU ('I owe you) in the form of a federal bond or other accounting instrument, then spending the money on unrelated current expenditures.
[citation needed] Net long-term capital gains as well as certain types of qualified dividend income are taxed preferentially.
The modern interpretation of the Sixteenth Amendment taxation power can be found in Commissioner v. Glenshaw Glass Co. 348 U.S. 426 (1955).
We would do violence to the plain meaning of the statute and restrict a clear legislative attempt to bring the taxing power to bear upon all receipts constitutionally taxable were we to say that the payments in question here are not gross income.
[55]In Conner v. The United States,[56] a couple had lost their home to a fire and had received compensation for their loss from the insurance company, partly in the form of hotel costs reimbursed.
The U.S. District Court acknowledged the authority of the IRS to assess taxes on all forms of payment but did not permit taxation on the compensation provided by the insurance company, because unlike a wage or a sale of goods at a profit, this was not a gain.
[60] At the beginning of the 20th century, President Theodore Roosevelt advocated the application of a progressive inheritance tax on the federal level.
In 2006, the IRS's National Taxpayer Advocate's report highlighted the AMT as the single most serious problem with the tax code.
[69] The end of the 1990s and the beginning of the present century heralded major reductions in taxing the income from gains on capital assets.