Taxation in Germany
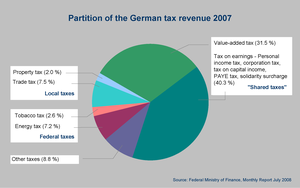
These taxes reflect Germany's commitment to a balanced approach between direct and indirect taxation, essential for funding extensive social welfare programs and public infrastructure.
The modern German tax system accentuate on fairness and efficiency, adapting to global economic trends and domestic fiscal needs.
The legal basis for taxation is established in the German Constitution (Grundgesetz), which lays out the basic principles governing tax law.
Generally, public and private corporations are liable for taxes in Germany, with certain exemptions such as charitable foundations and religious institutions.
Products and services generated in Germany are subject to value-added tax (VAT) under EU rules, with certain exemptions.
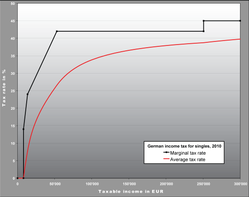
This progression ensures that the tax burden aligns with the ability to pay, reflecting principles of vertical equity.
[3] A freelancer in Germany might have a different set of tax considerations, particularly regarding allowable deductions such as business expenses.
[7] The German Constitution lays down the principles governing taxation in the following articles: When calculating the tax liability, the taxpayer may claim tax-reducing personal characteristics, e.g. special expenses, extraordinary burdens.
The German Fiscal Code (Abgabenordnung, AO) is divided into nine parts, which essentially reflect the chronological sequence of the taxation procedure.
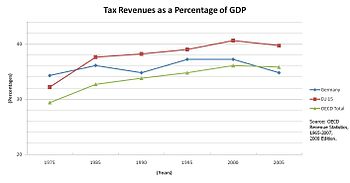
[10] According to the latest Revenue Statistics report published by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Germany has seen a significant increase in its tax-to-GDP ratio.
Habitual residence within the scope of the Tax Act shall always be deemed to be a continuous stay of more than six months from the beginning; short-term interruptions shall not be taken into consideration.
These include the debts and pension obligations of the East German government, as well as the costs of upgrading infrastructure and environmental remediation in the new states of Germany.
Non-resident real estate investors are also obliged to file a German property tax return each year.
It is important to note that German real estate owners are liable for taxation regardless of their tax residency status.
The basic structure of the double taxation agreements which Germany has signed follows the Model Tax Convention drawn up by the OECD.
In particular, the exchange of information between tax authorities is an important element in detecting and combating tax evasion and avoidance and in enabling accurate taxation.Doppelbesteuerungsabkommen und andere Abkommen im Steuerbereich - Bundesfinanzministerium - Themen Employment income earned in Germany is subject to different insurance contributions covering health, pension, nursing and unemployment insurance.
Taxable profits are determined using the result posted in the annual accounts (balance sheet and Income statement) drawn up under the Commercial Code.
In contrast to the latter, trade tax is charged by the local authorities or municipalities, who are entitled to the entire amount.
On the basis of the collecting rate (Hebesatz) in force in its area, the local authority calculates the trade tax payable.
This is because properties are taxed based on their value from the early 1960s (1930s in East Germany), violating the horizontal equity principle.
This tax applies to gains generated on real estate investments, if sold less than ten years after purchase.
Depreciation deductions of prior years are added to the sales price of the home, to derive a higher taxable gain.
The DTV is only suitable for financial institutions that regularly submit a large number of applications for reimbursement of German capital gains tax (KapSt) and solidarity surcharge (SolZ) on behalf of their customers residing abroad.
[21] As a matter of principle, all services and products generated in Germany by a business entity are subject to value-added tax (VAT).
Certain goods and services are exempted from value-added tax by law; this applies for German and foreign businesses alike.
[24] The overall intended effect of the reduction, stimulating the economy, was marginal[citation needed][25] and further diminished by the costs of adjusting prices (which not all businesses did), changing sales and billing systems, and doing that twice in such a short time.
It is levied depending on the type of vehicle (car, motorcycle, commercial truck, trailer, motorhome, etc.).
This approach ensures that both earners face equal average and marginal tax rates, regardless of how income is distributed between them.
In 2022, families with children also receive a one-time bonus of EUR 100 per child, which does not reduce the basic income support for jobseekers.
Since 2020, the standard tax allowance for single parents was raised to EUR 4,008, initially as a temporary response to pandemic-related challenges through 2020 and 2021, and made permanent from 2022 onward to support single-parent families.