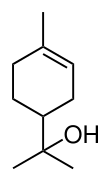
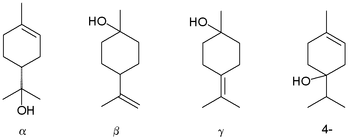
Terpineol
Terpenoids are terpene that are modified by the addition of a functional group, in this case, an alcohol.
β-Terpineol and γ-terpineol differ only by the location of the double bond.
Terpineol has a pleasant odor similar to lilac and is a common ingredient in perfumes, cosmetics, and flavors.
Although it is naturally occurring, terpineol is commonly manufactured from alpha-pinene, which is hydrated in the presence of sulfuric acid.
[4] An alternative route starts from limonene:[5] Limonene reacts with trifluoroacetic acid in a Markovnikov addition to a trifluoroacetate intermediate, which is easily hydrolyzed with sodium hydroxide to α-terpineol with 7% selectivity.