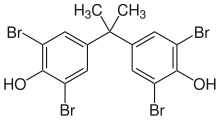
Tetrabromobisphenol A
Most commercial TBBPA products consist of a mixture that differ in the degree of bromination with the formula C15H16−xBrxO2 where x = 1 to 4.
A lower grade of TBBPA is used to prepare epoxy resins, used in printed circuit boards.
The study, which examined at 344 food samples from the fish and other seafood food group, concluded that “current dietary exposure to TBBPA in the European Union does not raise a health concern.” EFSA also determined that “additional exposure, particularly of young children, to TBBPA from house dust is unlikely to raise a health concern”.
[5] Further, TBBPA structurally mimics the thyroid hormone thyroxin (T4) and can bind more strongly to the transport protein transthyretin than T4 does, likely interfering with normal T4 activity.
Exposures of the general population are also well below the derived-no-effect-levels (DNELs) derived for endpoints of potential concern in REACH.
[11] TBBPA has been the subject of an eight-year evaluation under the EU Risk Assessment procedure which reviewed over 460 studies.