Estrogen
Once inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen receptors (ERs) which in turn modulate the expression of many genes.
Estrogens are among the wide range of endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs) and can cause health issues and reproductive disfunction in both wildlife and humans.
However, during pregnancy this role shifts to estriol, and in postmenopausal women estrone becomes the primary form of estrogen in the body.
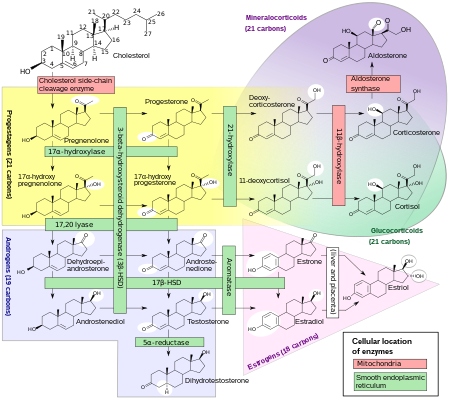
All of the different forms of estrogen are synthesized from androgens, specifically testosterone and androstenedione, by the enzyme aromatase.
[citation needed] Minor endogenous estrogens, the biosyntheses of which do not involve aromatase, include 27-hydroxycholesterol, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), 7-oxo-DHEA, 7α-hydroxy-DHEA, 16α-hydroxy-DHEA, 7β-hydroxyepiandrosterone, androstenedione (A4), androstenediol (A5), 3α-androstanediol, and 3β-androstanediol.
They promote the development of female secondary sexual characteristics, such as breasts, darkening and enlargement of nipples,[21] and thickening of the endometrium and other aspects of regulating the menstrual cycle.
In males, estrogen regulates certain functions of the reproductive system important to the maturation of sperm[22][23][24] and may be necessary for a healthy libido.
Conversely, androgens are responsible for pubic and body hair growth, as well as acne and axillary odor.
[48][49] Estrogen is primarily and directly responsible for inducing the ductal component of breast development,[50][51][52] as well as for causing fat deposition and connective tissue growth.
[50][51] It is also indirectly involved in the lobuloalveolar component, by increasing progesterone receptor expression in the breasts[50][52][53] and by inducing the secretion of prolactin.
[citation needed] Estrogen regulated DNA repair mechanisms in the brain have neuroprotective effects.
These scores vary in direct proportion to estrogen levels throughout the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause.
[63] Studies have also shown that the Met allele gene and level of estrogen mediates the efficiency of prefrontal cortex dependent working memory tasks.
Clinical recovery from postpartum, perimenopause, and postmenopause depression has been shown to be effective after levels of estrogen were stabilized and/or restored.
[71] Compulsions in male lab mice, such as those in obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), may be caused by low estrogen levels.
When estrogen levels were raised through the increased activity of the enzyme aromatase in male lab mice, OCD rituals were dramatically decreased.
Women exhibiting binge eating behaviors are found to have increased brain uptake of neuron 5-HT, and therefore less of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Research has predicted increased emotional eating during hormonal flux, which is characterized by high progesterone and estradiol levels that occur during the mid-luteal phase.
These effects produce menstrual cycle changes, which result in hormone release leading to behavioral changes, notably binge and emotional eating.
[78] Klump et al.[79] Progesterone may moderate the effects of low estradiol (such as during dysregulated eating behavior), but that this may only be true in women who have had clinically diagnosed binge episodes (BEs).
[78][80][81] In rodents, estrogens (which are locally aromatized from androgens in the brain) play an important role in psychosexual differentiation, for example, by masculinizing territorial behavior;[82] the same is not true in humans.
[citation needed] Women are less impacted by heart disease due to vasculo-protective action of estrogen which helps in preventing atherosclerosis.
[86] It also helps in maintaining the delicate balance between fighting infections and protecting arteries from damage thus lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease.
[93] Ligation of these receptors allows them to translocate to the nucleus and act as transcription factors either by binding estrogen response elements (ERE) on DNA or binding DNA together with other transcriptional factors e.g. Nf-kB or AP-1, both of which result in RNA polymerase recruitment and further chromatin remodelation.
This compound crosses the basal membrane into the surrounding granulosa cells, where it is converted either immediately into estrone, or into testosterone and then estradiol in an additional step.
Estrogens are inactivated primarily by the kidneys and liver and excreted via the gastrointestinal tract[101] in the form of conjugates, found in feces, bile, and urine.
[citation needed] In 1929, Adolf Butenandt and Edward Adelbert Doisy independently isolated and purified estrone, the first estrogen to be discovered.
Examples include estriol glucuronide (Emmenin, Progynon), estradiol benzoate, conjugated estrogens (Premarin), diethylstilbestrol, and ethinylestradiol.
A range of synthetic and natural substances that possess estrogenic activity have been identified in the environment and are referred to xenoestrogens.
[114] In 1993, the FDA determined that not all over-the-counter topically applied hormone-containing drug products for human use are generally recognized as safe and effective and are misbranded.