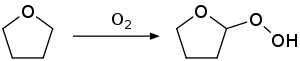Tetrahydrofuran
[8] DuPont developed a process for producing THF by oxidizing n-butane to crude maleic anhydride, followed by catalytic hydrogenation.
[11][12] This allows certain sugars to be converted to THF via acid-catalyzed digestion to furfural and decarbonylation to furan,[13] although this method is not widely practiced.
In the presence of strong acids, THF converts to a linear polymer called poly(tetramethylene ether) glycol (PTMEG), also known as polytetramethylene oxide (PTMO): This polymer is primarily used to make elastomeric polyurethane fibers like Spandex.
[14] The other main application of THF is as an industrial solvent for polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and in varnishes.
[15] THF is water-miscible and can form solid clathrate hydrate structures with water at low temperatures.
[16] THF has been explored as a miscible co-solvent in aqueous solution to aid in the liquefaction and delignification of plant lignocellulosic biomass for production of renewable platform chemicals and sugars as potential precursors to biofuels.
Commercial THF contains substantial water that must be removed for sensitive operations, e.g. those involving organometallic compounds.
Although THF is traditionally dried by distillation from an aggressive desiccant such as elemental sodium, molecular sieves have been shown to be superior water scavengers.
[20] In the presence of a solid acid catalyst, THF reacts with hydrogen sulfide to give tetrahydrothiophene.
[5][25] Reflecting its remarkable solvent properties, it penetrates the skin, causing rapid dehydration.