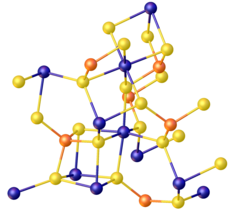
Thiosilicate
Derivatives where some sulfide is replaced by oxide are also called thiosilicates, examples being materials derived from the oxohexathiodisilicate [Si2OS6]6−.
Silicon is tetrahedral in all thiosilicates and sulfur is bridging or terminal.
Formally such materials are derived from silicon disulfide in analogy to the relationship between silicon dioxide and silicates.
Thiosilicates are typically encountered as colorless solids.
[2] Thiosilicates and related thiogermanates are also of interest for infrared optics, since they only absorb low frequency IR modes.