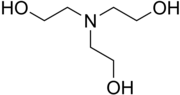
Triethanolamine
The triethanolamine neutralizes fatty acids, adjusts and buffers the pH, and solubilizes oils and other ingredients that are not completely soluble in water.
It facilitates the grinding process by preventing agglomeration and coating of the powder at the surface of balls and mill wall.
[6] Various ear diseases and infections are treated with eardrops containing triethanolamine polypeptide oleate-condensate, such as Cerumenex in the United States.
Exposure to TEOA resulted in focal inflammation, starting in single male animals from 20 mg/m3 concentrations.
[14] A 2009 study stated that patch test reactions reveal a slight irritant potential instead of a true allergic response in several cases, and also indicated the risk of skin sensitization to TEOA seems to be very low.
"[16] A 2009 study found that TEOA has potential acute, sub-chronic and chronic toxicity properties in respect to aquatic species.
[17] TEOA is listed under Schedule 3, part B of the Chemical Weapons Convention as it can be used in the manufacture of HN3 nitrogen mustard.