Winding number
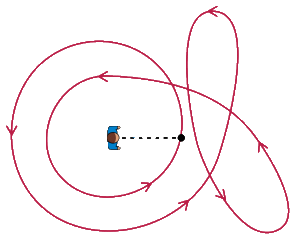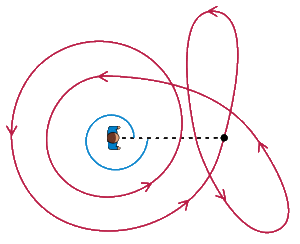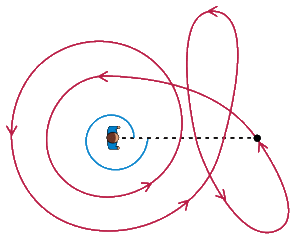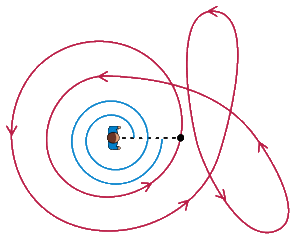
In mathematics, the winding number or winding index of a closed curve in the plane around a given point is an integer representing the total number of times that the curve travels counterclockwise around the point, i.e., the curve's number of turns.
For certain open plane curves, the number of turns may be a non-integer.
Winding numbers are fundamental objects of study in algebraic topology, and they play an important role in vector calculus, complex analysis, geometric topology, differential geometry, and physics (such as in string theory).
Suppose we are given a closed, oriented curve in the xy plane.
Using this scheme, a curve that does not travel around the origin at all has winding number zero, while a curve that travels clockwise around the origin has negative winding number.
be a continuous closed path on the plane minus one point.
Winding number is often defined in different ways in various parts of mathematics.
All of the definitions below are equivalent to the one given above: A simple combinatorial rule for defining the winding number was proposed by August Ferdinand Möbius in 1865[1] and again independently by James Waddell Alexander II in 1928.
[2] Any curve partitions the plane into several connected regions, one of which is unbounded.
The winding numbers of the curve around two points in the same region are equal.
Finally, the winding numbers for any two adjacent regions differ by exactly 1; the region with the larger winding number appears on the left side of the curve (with respect to motion down the curve).
We can therefore express the winding number of a differentiable curve as a line integral: The one-form dθ (defined on the complement of the origin) is closed but not exact, and it generates the first de Rham cohomology group of the punctured plane.
In particular, if ω is any closed differentiable one-form defined on the complement of the origin, then the integral of ω along closed loops gives a multiple of the winding number.
Winding numbers play a very important role throughout complex analysis (c.f.
In the context of complex analysis, the winding number of a closed curve
as[4] This is a special case of the famous Cauchy integral formula.
; (ii) constant over each component (i.e., maximal connected subset) of
As an immediate corollary, this theorem gives the winding number of a circular path
In topology, the winding number is an alternate term for the degree of a continuous mapping.
The above example of a curve winding around a point has a simple topological interpretation.
Maps from the 3-sphere to itself are also classified by an integer which is also called the winding number or sometimes Pontryagin index.
As a path followed through time, this would be the winding number with respect to the origin of the velocity vector.
In this case the example illustrated at the beginning of this article has a winding number of 3, because the small loop is counted.
This is called the turning number, rotation number,[6] rotation index[7] or index of the curve, and can be computed as the total curvature divided by 2π.
Turning number cannot be defined for space curves as degree requires matching dimensions.
However, for locally convex, closed space curves, one can define tangent turning sign as
is the turning number of the stereographic projection of its tangent indicatrix.
Its two values correspond to the two non-degenerate homotopy classes of locally convex curves.
Generally, the ray casting algorithm is a better alternative to the PIP problem as it does not require trigonometric functions, contrary to the winding number algorithm.
Nevertheless, the winding number algorithm can be sped up so that it too, does not require calculations involving trigonometric functions.