Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy.
[1] On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the troposphere,[2][3] just below the stratosphere.
Weather systems in the middle latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet streamflow.
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location.
A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years.
A star's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System.
On Earth, common weather phenomena include wind, cloud, rain, snow, fog and dust storms.
[5] Weather occurs primarily due to air pressure, temperature and moisture differences from one place to another.
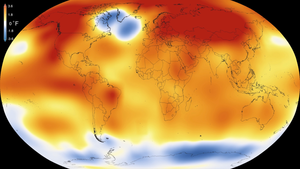
In other words, the farther from the tropics one lies, the lower the sun angle is, which causes those locations to be cooler due to the spread of the sunlight over a greater surface.
[6] The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the large scale atmospheric circulation cells and the jet stream.
[7] Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow (see baroclinity).
[11] The uneven solar heating (the formation of zones of temperature and moisture gradients, or frontogenesis) can also be due to the weather itself in the form of cloudiness and precipitation.
[20] During rains precipitation, the water droplets absorb and dissolve carbon dioxide from the surrounding air.
In the United States, the National Weather Service has an annual report for fatalities, injury, and total damage costs which include crop and property.
As of 2019, tornadoes have had the greatest impact on humans with 42 fatalities while costing crop and property damage over 3 billion dollars.
Aside from climatic changes that have caused the gradual drift of populations (for example the desertification of the Middle East, and the formation of land bridges during glacial periods), extreme weather events have caused smaller scale population movements and intruded directly in historical events.
One such event is the saving of Japan from invasion by the Mongol fleet of Kublai Khan by the Kamikaze winds in 1281.
[28] These included droughts, storms and unseasonal blizzards, as well as causing the Swiss Grindelwald Glacier to expand.
[29] Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location.
Human beings have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since at least the nineteenth century.
[37][38] Forecasts based on temperature and precipitation are important to agriculture,[39][40][41][42] and therefore to commodity traders within stock markets.
Because of these two factors, clouds and rainstorms in the tropics can occur more spontaneously compared to those at higher latitudes, where they are more tightly controlled by larger-scale forces in the atmosphere.
[46] The aspiration to control the weather is evident throughout human history: from ancient rituals intended to bring rain for crops to the U.S. Military Operation Popeye, an attempt to disrupt supply lines by lengthening the North Vietnamese monsoon.
[48] Whereas there is inconclusive evidence for these techniques' efficacy, there is extensive evidence that human activity such as agriculture and industry results in inadvertent weather modification:[47] The effects of inadvertent weather modification may pose serious threats to many aspects of civilization, including ecosystems, natural resources, food and fiber production, economic development, and human health.
[65] One of the most famous landmarks in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years.
Like all stars, the Sun's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System.