Wind power in Maine
Download coordinates as: There are a number of wind power projects in the state of Maine, totaling more than 900 megawatts (MW) in capacity.
[3] In 2008, then-Governor John Baldacci set a goal for the state of 2,000 megawatts of wind power installed by 2015 and 3,000 MW by 2020.
Paul LePage created a moratorium on all new wind power construction stating, “While out-of-state interests are eager to exploit our western mountains in order to serve their political agendas, we must act judiciously to protect our natural beauty.
It generates approximately 167 million kilowatt-hours (kW·h) of electricity per year and began commercial operations in January 2009.
[12] In March 2009, the Maine Land Use Regulation Committee (LURC) approved First Wind's $60 million 25.5 MW Stetson II expansion.
Approved by a vote of 383–5 on July 29, 2008 by members of the Fox Islands Electric Cooperative, construction began on June 29, 2009, and the wind farm went online on November 17.
[45] The University of Maine Advanced Structures and Composites Center has led efforts to develop this resource with its patented floating wind turbine technology, VolturnUS.
[47] The VolturnUS is a floating concrete hull design that can support a wind turbine in waters 45 meters deep or more.
In 2013 a 1:8th scale VolturnUS hull with a 65 feet (20 m) tall turbine was towed into Penobscot Bay near Castine, Maine where it was connected to the grid and tested for 18 months.
New England Aqua Ventus I is anticipated to be the first commercial-scale floating wind project in the United States.
A new 345 kV tramission line will connect it to the ISO New England grid, and 40% of electricity will be purchased by utilities in Massachusetts.
[50] In 2005, Maine Mountain Power (MMP) filed an application with the Maine Land Use Regulation Committee (LURC) for a permit to develop a 30-turbine wind farm on Mount Redington (45°1.50′N 70°23.32′W / 45.02500°N 70.38867°W / 45.02500; -70.38867 (Mount Redington)) and neighboring Black Nubble (45°1.92′N 70°26.83′W / 45.03200°N 70.44717°W / 45.03200; -70.44717 (Black Nubble)).
The summit of Redington was seen as too ecologically sensitive — a sub-alpine fir habitat providing a home for two rare species, the bog lemming and Bicknell's thrush.
[53][54][55] A revised proposal, for 18 turbines only on Black Nubble, was put forward by MMP, supported by many environmental groups,[53][56] but still opposed by Maine Audubon.
[citation needed] The developer placed the project on hold due to the strength of wind gusts in the area.
[59] In April 2012, Statoil, a Norwegian multinational oil and gas company, received state regulatory approval to build a large four-unit demonstration floating wind farm off the coast of Maine called Hywind 2.
[61][62] The State of Maine Public Utility Commission voted to approve the construction and fund the US$120 million project by adding approximately 75 cents/month to the average retail electricity consumer.
The legislation required the Maine Public Utilities Commission to undertake a second round of bidding with a different set of ground rules; that led Statoil to suspend the project due to increased uncertainty and risk.
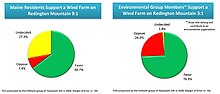
[64] A statewide poll in Spring 2007 by the Pan Atlantic SMS Group showed that 85% of Maine people supported wind power development.
[65] A 2009 poll conducted by Portland-based Critical Insights shows that 90% of Maine people support the development of wind power as a source of electricity.
Calls to residents in seven rural counties, from Aroostook to Oxford, where most wind power projects are built or planned, showed 83 percent support.
Survey results show that Maine residents strongly support wind power development, chiefly because it cuts dependence on fossil fuels and creates jobs.