Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008 was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and officially launched on the 27th of that month.
Since the codebase is common, Windows Server 2008 inherits most of the technical, security, management and administrative features new to Windows Vista such as the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, event logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and address space layout randomization (ASLR); the improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .NET Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the core kernel, memory and file system improvements.
All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
[19] Windows Server 2008 offers high availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering.
CPU time, bandwidth that it can use, number of processors it can be run on, and allocated to a process can be restricted.
The IA-64 variant is optimized for high-workload scenarios like database servers and Line of Business (LOB) applications.
[37] Editions of Windows Server 2008 include:[38] The Microsoft Imagine program, known as DreamSpark at the time, used to provide verified students with the 32-bit variant of Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, but the version has since then been removed.
The Server Core feature is available in the Web, Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter editions.
Service Pack 2 added new features, such as Windows Search 4.0, support for Bluetooth 2.1, the ability to write to Blu-ray discs, and simpler Wi-Fi configuration.
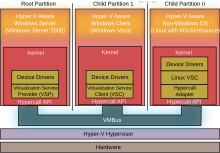
Windows Server 2008 specifically received the final release of Hyper-V 1.0, improved backwards compatibility with Terminal Server license keys and an approximate 10% reduction in power usage with this service pack.
[58] Starting in March 2019, Microsoft began transitioning to exclusively signing Windows updates with the SHA-2 algorithm.
As a result of this Microsoft released several updates throughout 2019 to add SHA-2 signing support to Windows Server 2008.
[59] In June 2018, Microsoft announced that they would be moving Windows Server 2008 to a monthly update model beginning with updates released in September 2018[60] – two years after Microsoft switched the rest of their supported operating systems to that model.
This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding "version-related issues".
[2] The last free security update rollup packages were released on January 14, 2020.
[65] Support for the RTM version of Windows Server 2008 ended on July 12, 2011,[4] and users can no longer receive further security updates for the operating system.
However, in order to give customers more time to migrate to newer Windows versions, particularly in developing or emerging markets, Microsoft decided to extend support to January 14, 2020.
[5][7][6] Windows Server 2008 was eligible for the paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program.
[5][66] Prior to the ESU program becoming available, Windows Server 2008 was eligible for the now discontinued, paid Premium Assurance program (an add-on to Microsoft Software Assurance) available to volume license customers.
[9][8][10][67] This will mark the final end of all security updates for the Windows NT 6.0 product line after 19 years, 2 months, and 5 days.