Windows Vista networking technologies
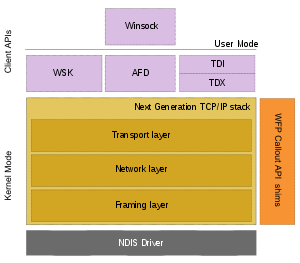
The new stack, implemented as a dual-stack model, depends on a strong host-model and features an infrastructure to enable more modular components that one can dynamically insert and remove.
A single icon in the notification area (system tray) represents connectivity through all network adapters, whether wired or wireless.
Windows Firewall and the IPsec Policies snap-in support IPv6 addresses as permissible character strings.
IPv6 can even be used when full native IPv6 connectivity is not available, using Teredo tunneling; this can even traverse most IPv4 symmetric Network Address Translations (NATs) as well.
This allows implementation of wireless-specific features such as larger frame sizes and optimized error recovery procedures.
Windows Vista also provides a Fast Roaming service that will allow users to move from one access point to another without loss of connectivity.
The machine will run a script, stored either on the system or on USB thumb drive, which authenticates it to the domain.
Authentication can be done either by using username and password combination or security certificates from a Public key infrastructure (PKI) vendor such as VeriSign.
Another significant change that aims to improve network throughput is the automatic resizing of TCP Receive window.
The sender detects the segment did not reach the destination; but due to lack of feedback from the congested router, it has no information on the extent of reduction in transmission rate it needs to make.
The sender then reduces the size of its congestion window, which is the limit on the amount of data in flight at any time.
Exponential backoff and only additive increase produce stable network behaviour, letting routers recover from congestion.
With ECN support enabled, the router sets two bits in the data packets that indicate to the receiver it is experiencing congestion (but not yet fully choked).
The advantage of this approach is that the router does not get full enough to drop packets, and thus the sender does not have to lower the transmission rate significantly to cause serious delays in time-sensitive streams; nor does it risk severe under-utilization of bandwidth.
Any router along the way can prevent the use of ECN if it considers ECN-marked packets invalid and drops them (or more typically the whole connection setup fails because of a piece of network equipment that drops connection setup packets with ECN flags set).
Windows Vista also supports network cards with TCP Offload Engine, that have certain hardware-accelerated TCP/IP-related functionality.
Support for 256-bit, 384-bit and 512-bit Elliptic curve Diffie–Hellman (ECDH) algorithms, as well as for 128-bit, 192-bit and 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is included in the network stack itself.
Computers running Windows Vista can be a part of logically isolated networks within an Active Directory domain.
Advanced firewall filtering rules (exceptions) and IPsec policies can be set up such as by domain, public, and private profiles, source and destination IP addresses, IP address range, source and destination TCP and UDP ports, all or multiple ports, specific types of interfaces, ICMP and ICMPv6 traffic by Type and Code, services, edge traversal, IPsec protection state and specified users and computers based on Active Directory accounts.
Windows Vista has a greater awareness of the network topology the host computer is in, using technologies such as Universal Plug and Play.
WFP allows incoming and outgoing packets to be filtered, analyzed or modified at several layers of the TCP/IP protocol stack.
Upon its initial release WFP was plagued with bugs including memory leaks and race conditions.
The API also allows creation of a secure overlay network called a Group, consisting of all or a subset of nodes in a Graph.
Another planned feature in Windows Vista would have provided a new domain-like networking setup known as a Castle, but this did not make it into the release.
Castle would have made it possible to have an identification service, which provides user authentication, for all members on the network, without a centralized server.
[15] People Near Me was listed as part of Microsoft's mobile platform strategy as revealed during the Windows Hardware Engineering Conference of 2004.
[18][19] The new Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) 3.0 in Windows Vista has a new feature called Neighbor Casting which supports peer-to-peer file transfers within a domain; this facilitates Peer Caching, allowing users to download and serve content (such as WSUS updates) from peers on the same subnet, receive notifications when a file is downloaded, access the temporary file while the download is in progress, and control HTTP redirects.
WinHTTP, the client API for server-based applications and services supports IPv6, AutoProxy, HTTP/1.1 chunked transfer encoding, larger data uploads, SSL and client certificates, server and proxy authentication, automatic handling of redirects and keep-alive connections and HTTP/1.0 protocol, including support for keep-alive (persistent) connections and session cookies.
While most of the same sockets programming concepts exist as in user-mode Winsock such as socket, creation, bind, connect, accept, send and receive, Winsock Kernel is a completely new programming interface with unique characteristics such as asynchronous I/O that uses IRPs and event callbacks to enhance performance.
The Windows Vista Bluetooth stack is improved with support for more hardware IDs, EDR performance improvements, Adaptive frequency hopping for Wi-Fi co-existence, and Synchronous Connection Oriented (SCO) protocol support which is needed for audio profiles.