ZFK equation
[1][2] The equation is analogous to KPP equation except that is contains an exponential behaviour for the reaction term and it differs fundamentally from KPP equation with regards to the propagation velocity of the traveling wave.
is the non-dimensional dependent variable (typically temperature) and
corresponds to KPP regime.
The minimum propagation velocity
(which is usually the long time asymptotic speed) of a traveling wave in the ZFK regime is given by whereas in the KPP regime, it is given by Similar to Fisher's equation, a traveling wave solution can be found for this problem.
Suppose the wave to be traveling from right to left with a constant velocity
The ZFK equation reduces to satisfying the boundary conditions
The boundary conditions are satisfied sufficiently smoothly so that the derivative
is obtained as part of the solution, thus constituting a nonlinear eigenvalue problem.
and the corresponding reaction term
is formally analyzed using activation energy asymptotics.
is negligible everywhere except in a thin layer close to the right boundary
The problem for outer region is given by The solution satisfying the condition
(an arbitrary choice) to fix the wave location somewhere in the domain because the problem is translationally invariant in the
, reaction term is no longer negligible.
To investigate the inner layer structure, one introduces a stretched coordinate encompassing the point
is approaching unity according to the outer solution and a stretched dependent variable according to
Substituting these variables into the governing equation and collecting only the leading order terms, we obtain The boundary condition as
comes from the local behaviour of the outer solution obtained earlier, which when we write in terms of the inner zone coordinate becomes
The first integral of the above equation after imposing these boundary conditions becomes which implies
It is clear from the first integral, the wave speed square
is proportional to integrated (with respect to
limit, only the inner zone contributes to this integral).
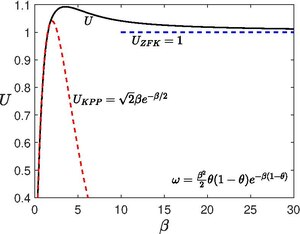
For the reaction term used here, the KPP speed that is applicable for
Numerical integration of the equation for various values of
showed that there exists a critical value
The region between the KPP regime and the ZFK regime is called the KPP–ZFK transition zone.
The critical value depends on the reaction model, for example we obtain To predict the KPP–ZFK transition analytically, Paul Clavin and Amable Liñán proposed a simple piecewise linear model[6] where
that mimics a sharp increase in the reaction near
For this model there exists a critical value