1,4-Butanediol
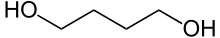
1,4-Butanediol, also called Butane-1,4-diol (other names include 1,4-B, BD, BDO and 1,4-BD),[5] is a primary alcohol and an organic compound with the formula HOCH2CH2CH2CH2OH.
It is a colorless viscous liquid first synthesized in 1890 via acidic hydrolysis of N,N'-dinitro-1,4-butanediamine by Dutch chemist Pieter Johannes Dekkers, who called it "tetramethylene glycol".
[9] It is also made on an industrial scale from maleic anhydride in the Davy process, which is first converted to the methyl maleate ester, then hydrogenated.
Butane-1,4-diol is used industrially as a solvent[additional citation(s) needed] and in the manufacture of some types of plastics, elastic fibers and polyurethanes.
In 2013, worldwide production was claimed to be billions of pounds (consistent with approximately one million metric tons).
Adverse effects in higher doses include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, sedation, vertigo, and potentially death if ingested in large amounts.
[25] A jury in Federal District Court in Chicago found that 1,4-butanediol was not an analog of GHB under federal law, which was not disputed on the case's appeal to the Seventh Circuit Court of Appeals, however this finding did not affect the outcome of the case.
[26] In the United Kingdom, 1,4-butanediol was scheduled in December 2009 (along with another GHB precursor, gamma-butyrolactone) as a Class C controlled substance.
A toy called "Bindeez" ("Aqua Dots" in North America) was recalled by the distributor in November 2007 because of the presence of butane-1,4-diol.
Seven showed severe symptoms, two were transported to a hospital in Frankfurt am Main, and a 30-year-old person was, for a time, in a critical state.