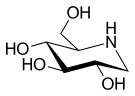
1-Deoxynojirimycin
[3] 1-Deoxynojirimycin is a polyhydroxylated piperidine alkaloid produced from D-Glucose in various plants, such as Commelina communis, and in the Streptomyces and Bacillus bacteria.
[4][5] High quantities of this azasugar are produced in Bacillus subtilis, a process initiated by a TYB gene cluster composed of gabT1 (aminotransferase), yktc1 (phosphatase), and gutB1 (oxidoreductase).
[8] Regio-selective oxidation by GutB1[7] occurs at the exposed C6 hydroxyl of ADM, pushing a C2-N-C6 cyclization of the resulting 6-oxo intermediate,[9] creating Manojirimycin (MJ).
[8] In the Streptomyces subrutilus species, a secondary pathway branching from the manojirimycin precursor results in 1-deoxymanojirimycin via dehydration and reduction of the isomer.
[4] Azasugar biosynthesis in Commelina communis involves C1-C5 cyclisation of the original D-glucose precursor without the subsequent inversion.