TransLink (British Columbia)
Major changes include new revenue-generating measures, a restructuring of the executive of the body, and increases in the areas under TransLink's jurisdiction.
"[10] British Columbia New Democratic Party critic David Chudnovsky responded that the reorganization was "ludicrous" and that its purpose was "to get power away from our elected municipal politicians because once in a while they disagree with the aggressive privatization agenda of Mr.
[12][13] On March 19, 2008, the Vancouver Sun reported that TransLink was launching a real estate division that could produce over $1.5 billion in revenue over the ensuing ten years.
[14] NDP critic Maurine Karagianis introduced a private member's bill dubbed the "TransLink Openness Act".
[15] In 2015, residents of Metro Vancouver were asked to vote in a mail-in plebiscite on a proposal to adopt a new 0.5 percent sales tax to fund improvements in transit infrastructure, and completion of current TransLink projects.
Opposition to the tax was headed by the Canadian Taxpayers Federation who drew the public's attention to purported misuse of funds by TransLink.
Surveys conducted by Insights West showed the Yes side ahead in December 2014, but support dropped to 37 per cent the week before the ballots were mailed.
[23] Phase one was scheduled to be rolled out between 2017 and 2026, and it included the launch of five new B-Lines, and service improvements on buses, SkyTrain, SeaBus, and HandyDART.
[27] McCallum had campaigned on cancelling the plans for light rail and instead extending the Expo Line from King George station to Langley.
[29] The existing funding would only extend the line 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) to Fleetwood in Surrey and add four new stations, terminating at 166th Street.
[30] The council also voted to proceed with preparing a detailed business case for the full Surrey–Langley SkyTrain extension, which was expected to be completed by early 2020.
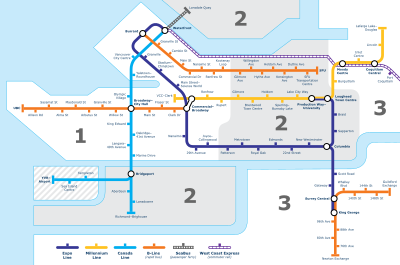
Outside the city of Vancouver, most buses operate on a hub-and-spoke system along feeder routes that connect with SkyTrain, SeaBus, West Coast Express, or other regional centres.
Some suburban routes use Orion highway coaches with high-back reclining seats, overhead reading lights and luggage racks.
Fare inspections on buses are normally conducted by Transit Security officers and on occasion by the South Coast British Columbia Transportation Authority Police Service.
TransLink also operates a late-night bus service, called NightBus, on 10 routes extending from downtown throughout the city and to several suburbs.
Construction on the Evergreen Extension of the Millennium Line began in 2012 and completed in 2016, expanding service from Lougheed Town Centre to Coquitlam.
SeaBus is a passenger ferry service across Burrard Inlet between Vancouver and the North Shore municipalities that is operated by Coast Mountain Bus Company and integrated with the transit system.
[51] A fare paid zone is a clearly marked territory on which passengers must have valid proof of payment and produce it for inspection upon request of a Transit Employee.
Fare inspections are conducted by the South Coast British Columbia Transportation Authority Police Service and Transit Security.
[62][63] On May 22, 2018, the ability to pay with contactless Visa and Mastercard credit cards (including mobile payment software) was added to Compass readers.
On March 20, 2020, TransLink suspended fare collection on all buses indefinitely in an effort to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic in the province, specifically to meet physical distancing requirements in combating the spread of COVID-19.
Part of the measures included allowing the boarding and alighting of passengers only via a bus' rear door, which lack the means to collect cash fares.
Transit security officers are mobile, ride buses and trains, inspect fares, issue fines and patrol TransLink properties.
This money is spread among capital and operating projects, with some allocated to cost-sharing programs, which result in additional investment in cycling.
TransLink also produces a regional cycling map, which is available for sale or as a free PDF file downloadable from its website.
TransLink installs and maintains bicycle parking racks and lockers at SkyTrain stations and transit interchanges through private contractors.
[94] Under the terms of provincial legislation, each year the screening panel prepares a shortlist of candidates for TransLink's board of directors.
Each of the following organizations must appoint one person to the Screening Panel: The board is responsible for hiring, compensating, and monitoring the performance of the CEO and for providing oversight of TransLink's strategic planning, finances, major capital projects, and operations.
[120] Prior to this time, the regional transportation commissioner approved all cash fare increases greater than the rate of inflation.
[121] The report also stated that the absence of mechanisms to "ensure accountability, effectiveness, and efficiency" made TransLink's governance "unique in the world and not in a good way".