3D reconstruction
[1] If the model is allowed to change its shape in time, this is referred to as non-rigid or spatio-temporal reconstruction.
[3] For instance, the lesion information of the patients can be presented in 3D on the computer, which offers a new and accurate approach in diagnosis and thus has vital clinical value.
[4] Digital elevation models can be reconstructed using methods such as airborne laser altimetry[5] or synthetic aperture radar.
A simple example of a mechanical method would use a depth gauge to measure a distance to a rotating object put on a turntable.
More applicable radiometric methods emit radiance towards the object and then measure its reflected part.
[9] Monocular cues methods refer to using one or more images from one viewpoint (camera) to proceed to 3D construction.
3D reconstruction through monocular cues is simple and quick, and only one appropriate digital image is needed thus only one camera is adequate.
[13] Shape-from-texture Suppose such an object with smooth surface covered by replicated texture units, and its projection from 3D to 2D causes distortion and perspective.
Distortion and perspective measured in 2D images provide the hint for inversely solving depth of normal information of the object surface.
Deep neural networks have shown to be highly effective for 3D reconstruction from a single color image.
[17] Stereo vision obtains the 3-dimensional geometric information of an object from multiple images based on the research of human visual system.
Binocular stereo vision method requires two identical cameras with parallel optical axis to observe one same object, acquiring two images from different points of view.
Binocular stereo vision method is well developed and stably contributes to favorable 3D reconstruction, leading to a better performance when compared to other 3D construction.
The approach of using Binocular stereo vision to acquire object's 3D geometric information is on the basis of visual disparity.
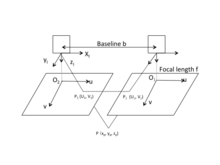
[19] The following picture provides a simple schematic diagram of horizontally sighted Binocular Stereo Vision, where b is the baseline between projective centers of two cameras.
There are various types of methods for image acquisition that depends on the occasions and purposes of the specific application.
Not only the requirements of the application must be met, but also the visual disparity, illumination, performance of camera and the feature of scenario should be considered.
Camera calibration in Binocular Stereo Vision refers to the determination of the mapping relationship between the image points
Camera calibration is a basic and essential part in 3D reconstruction via Binocular Stereo Vision.
The aim of feature extraction is to gain the characteristics of the images, through which the stereo correspondence processes.
Certain interference factors in the scenario should be noticed, e.g. illumination, noise, surface physical characteristic, etc.
According to precise correspondence, combined with camera location parameters, 3D geometric information can be recovered without difficulties.
Clinical routine of diagnosis, patient follow-up, computer assisted surgery, surgical planning etc.
Existing Approaches: Delaunay and alpha-shapes Both methods have been recently extended for reconstructing point clouds with noise.
Loss of the geometry precision in areas with extreme curvature, i.e., corners, edges is one of the main issues encountered.
Furthermore, pretreatment of information, by applying some kind of filtering technique, also affects the definition of the corners by softening them.
There are several studies related to post-processing techniques used in the reconstruction for the detection and refinement of corners but these methods increase the complexity of the solution.
Since the technique needs enormous amount of calculations, which requires strong configuration computers is appropriate for low contrast data.
To obtain internal points average has a higher computational cost, but offers better results.
The Voxel Grid method presents the same problems as other filtering techniques: impossibility of defining the final number of points that represent the surface, geometric information loss due to the reduction of the points inside a voxel and sensitivity to noisy input spaces.