Dopamine
[25] Dopamine is broken down into inactive metabolites by a set of enzymes—monoamine oxidase (MAO), catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT), and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), acting in sequence.
[29][30] Although dopamine is normally broken down by an oxidoreductase enzyme, it is also susceptible to oxidation by direct reaction with oxygen, yielding quinones plus various free radicals as products.
[50] Dopamine produced by neurons in the arcuate nucleus is secreted into the hypophyseal portal system of the median eminence, which supplies the pituitary gland.
[50] The zona incerta, grouped between the arcuate and periventricular nuclei, projects to several areas of the hypothalamus, and participates in the control of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, which is necessary to activate the development of the male and female reproductive systems, following puberty.
[56] In the opposite direction, drugs that increase dopamine release, such as cocaine or amphetamine, can produce heightened levels of activity, including, at the extreme, psychomotor agitation and stereotyped movements.
[53] When an action is followed by an increase in dopamine activity, the basal ganglia circuit is altered in a way that makes the same response easier to evoke when similar situations arise in the future.
[58] Evidence from microelectrode recordings from the brains of animals shows that dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra are strongly activated by a wide variety of rewarding events.
[58] These reward-responsive dopamine neurons in the VTA and substantia nigra are crucial for reward-related cognition and serve as the central component of the reward system.
[59][61][66] For example, direct electrical stimulation of dopamine pathways, using electrodes implanted in the brain, is experienced as pleasurable, and many types of animals are willing to work to obtain it.
[71][72] This research demonstrated that increased dopamine neurotransmission acts as a sine qua non condition for pleasurable hedonic reactions to music in humans.
[75] Beyond its role in modulating blood flow, there are several peripheral systems in which dopamine circulates within a limited area and performs an exocrine or paracrine function.
Hence, defects in renal dopamine function can lead to reduced sodium excretion and consequently result in the development of high blood pressure.
There is strong evidence that faults in the production of dopamine or in the receptors can result in a number of pathologies including oxidative stress, edema, and either genetic or essential hypertension.
[26] When L-DOPA is administered regularly over a long time period, a variety of unpleasant side effects such as dyskinesia often begin to appear; even so, it is considered the best available long-term treatment option for most cases of Parkinson's disease.
[26] Other drugs that enhance dopamine function, such as bromocriptine and pergolide, are also sometimes used to treat Parkinsonism, but in most cases L-DOPA appears to give the best trade-off between positive effects and negative side-effects.
[102] Cocaine, substituted amphetamines (including methamphetamine), Adderall, methylphenidate (marketed as Ritalin or Concerta), and other psychostimulants exert their effects primarily or partly by increasing dopamine levels in the brain by a variety of mechanisms.
At the earliest stage, genetic differences that alter the expression of dopamine receptors in the brain can predict whether a person will find stimulants appealing or aversive.
[104] Finally, the chronic elevation in dopamine that comes with repetitive high-dose stimulant consumption triggers a wide-ranging set of structural changes in the brain that are responsible for the behavioral abnormalities which characterize an addiction.
[117] Psychiatrists in the early 1950s discovered that a class of drugs known as typical antipsychotics (also known as major tranquilizers), were often effective at reducing the psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia.
[120] The dopamine hypothesis drew additional support from the observation that psychotic symptoms were often intensified by dopamine-enhancing stimulants such as methamphetamine, and that these drugs could also produce psychosis in healthy people if taken in large enough doses.
[125] Some of the most effective therapeutic agents for ADHD are psychostimulants such as methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) and amphetamine (Evekeo, Adderall, Dexedrine), drugs that increase both dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain.
[123][126][127] Dopamine plays a role in pain processing in multiple levels of the central nervous system including the spinal cord, periaqueductal gray, thalamus, basal ganglia, and cingulate cortex.
[137] This dates the emergence of dopamine as a neurotransmitter back to the earliest appearance of the nervous system, over 500 million years ago in the Cambrian Period.
[135] As in all vertebrates – invertebrates such as roundworms, flatworms, molluscs and common fruit flies can all be trained to repeat an action if it is consistently followed by an increase in dopamine levels.
[145] The functions of plant catecholamines have not been clearly established, but there is evidence that they play a role in the response to stressors such as bacterial infection, act as growth-promoting factors in some situations, and modify the way that sugars are metabolized.
[146] In a species of marine green algae Ulvaria obscura, a major component of some algal blooms, dopamine is present in very high concentrations, estimated at 4.4% of dry weight.
[152] The complex patterns that appear on butterfly wings, as well as black-and-white stripes on the bodies of insect larvae, are also thought to be caused by spatially structured accumulations of dopamine-melanin.
[153] Dopamine was first synthesized in 1910 by George Barger and James Ewens at Wellcome Laboratories in London, England[154] and first identified in the human brain by Katharine Montagu in 1957.
Dopamine's function as a neurotransmitter was first recognized in 1958 by Arvid Carlsson and Nils-Åke Hillarp at the Laboratory for Chemical Pharmacology of the National Heart Institute of Sweden.
[155] Carlsson was awarded the 2000 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for showing that dopamine is not only a precursor of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline), but is also itself a neurotransmitter.
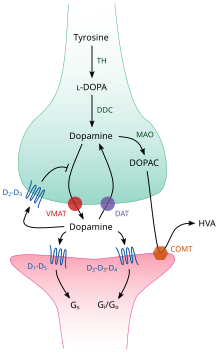
TH: tyrosine hydroxylase
DOPA: L-DOPA
DAT: dopamine transporter
DDC: DOPA decarboxylase
VMAT: vesicular monoamine transporter 2
MAO: Monoamine oxidase
COMT: Catechol-O-methyl transferase
HVA: Homovanillic acid






