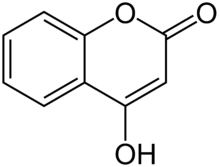
4-Hydroxycoumarin
This happens in the presence of naturally occurring formaldehyde, which allows attachment of a second 4-hydroxycoumarin molecule through the linking carbon of the formaldehyde, to the 3-position of the first 4-hydroxycoumarin molecule, to give the semi-dimer the motif of the drug class.
Dicoumarol appears as a fermentation product in spoiled sweet clover silages and is considered a mycotoxin.
[2] After the identification of dicoumarol and its anticoagulant activity, it became the prototype for a class of drugs.
4-Hydroxycoumarin forms the core of the chemical structure of anticoagulants known collectively as 4-hydroxycoumarins.
They include, for example, warfarin, a pharmaceutical drug used to prevent formation of blood clots, and brodifacoum, a widely used rodenticide.