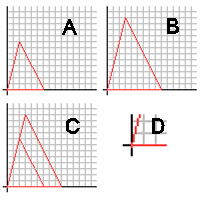
AA postulate
In Euclidean geometry, the AA postulate states that two triangles are similar if they have two corresponding angles congruent.
The AA postulate follows from the fact that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always equal to 180°.
(This is sometimes referred to as the AAA Postulate—which is true in all respects, but two angles are entirely sufficient.)
If they are aligned, as in grid C, it is apparent that the angle on the origin is congruent with the other (D).
We know this because the pairs of sides around them are similar, stem from the same point, and line up with each other.