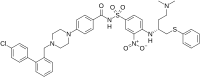
ABT-737
ABT-737 is a small molecule drug that inhibits Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, two members of the Bcl-2 family of evolutionarily-conserved proteins that share Bcl-2 Homology (BH) domains.
[2] The Bcl-2 family is most notable for their regulation of apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, at the mitochondrion; Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL are anti-apoptotic proteins.
Because many cancers have mutations in these genes that allow them to survive, scientists began working to develop drugs that would inhibit this pathway in the 1990s.
[3] In animal models, it improved survival, caused tumor regression, and cured a high percentage of mice.
[4] In preclinical studies utilizing patient xenografts, ABT-737 showed efficacy for treating lymphoma and other blood cancers.