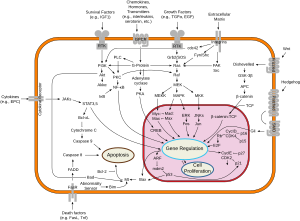
Bcl-xL
However, if Bax and Bak become activated, and Bcl-xL is sequestered away by gatekeeper BH3-only factors (e.g. Bim) causing a pore to form, cytochrome c is released leading to initiation of caspase cascade and apoptotic events.
Bcl-xL is about ten times more functional than Bcl-2 when induced by the chemotherapy drug, Doxorubicin[3] and can specifically bind to cytochrome C residues, preventing apoptosis.
[5] Bcl-xL dysfunction in mice can cause ineffective production of red blood cells, severe anemia, hemolysis, and death.
[7] Similar to other Bcl-2 family members, Bcl-xL has been implicated in the survival of cancer cells by inhibiting the function of p53, a tumor suppressor.
In cancerous mouse cells, those which contained Bcl-xL were able to survive while those that only expressed p53 died in a small period of time.